What is Ultrasound
In this procedure, high-energy sound waves are used to visualize the tissues and organs inside the body. Sound waves create echoes that create pictures of tissues and organs on a computer screen.
Ultrasound is used to help diagnose very dangerous diseases like cancer etc. It is also used during pregnancy to examine the fetus and during medical procedures such as biopsy.
USES OF ULTRASOUND
Ultrasound is a type of sound wave that is used in a variety of medical procedures. This wave is created by a machine that sends out a pulse of energy.
When this pulse hits a body part, it causes the tissue to vibrate. This vibration creates the ultrasound waves. These waves can be used to create images of the inside of the body or to treat medical conditions.

Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
Ultrasound is a type of energy that is used in a variety of medical procedures. This energy is high frequency and is used to create images of the inside of the body. Ultrasound is also used to treat a variety of medical conditions.
Working principle of Ultrasound
Ultrasound technology is a commonly used medical diagnostic tool. Its working principle is based on the transmission of high-frequency sound waves through the body to create images of the internal organs.
Ultrasound is a safe and non-invasive procedure that does not use radiation.

Ultrasound is a diagnostic tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body.
These images can be used to assess the health of organs and tissues. Ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure, and it does not use radiation.
Ultrasounds are a type of medical imaging that use high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body.
They are used to help diagnose a variety of medical conditions. There are several different types of ultrasound, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.

The most common type of ultrasound is an abdominal ultrasound. This ultrasound is used to examine the organs in the abdomen, such as the liver, kidneys, and pancreas.
Abdominal ultrasounds are typically used to diagnose conditions such as gallstones, liver cancer, and pancreatitis.
Other common types of ultrasounds include pelvic ultrasounds and transvaginal ultrasounds. Pelvic ultrasounds are used to examine the organs in the pelvis, such as the uterus, ovaries, and bladder.
They are typically used to diagnose conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease, ovarian cancer, and uterine cancer.
Transvaginal ultrasounds are used to examine the female reproductive organs, including the vagina, uterus, and ovaries. They are typically used to diagnose conditions such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, and cervical cancer.
TYPES OF ULTRASOUND
There are also several specialized types of ultrasounds, such as echocardiograms, which are used to examine the heart.
1. Abdominal Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound helps the doctor evaluate the cause of abdominal pain or bloating. It also helps in the detection of kidney stones, liver disease, tumors and many other conditions. If you are at risk of an abdominal aortic aneurysm, your doctor may recommend an abdominal ultrasound. Pelvic Ultrasound
2. What can an abdominal ultrasound detect?
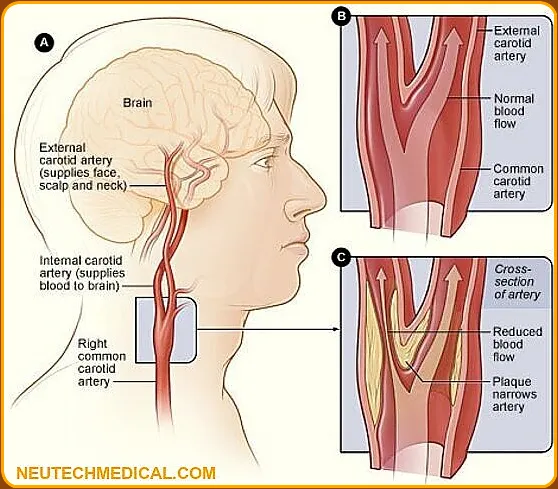
It is used to evaluate vascular ultrasound: blood flow in the arteries in your neck that supply blood to the brain. The blood flows to a newly transplanted organ.
It measures blood flow in the arteries to determine the presence, severity, and specific location of a narrowed area of the artery.
3. Transabdominal Ultrasound
Most importantly, a transabdominal ultrasound is commonly used in pregnant women to monitor the development of the baby at or before 14 weeks of pregnancy.
For this type of ultrasound, the technician will put a small amount of warm gel on the patient or your abdomen and move the probe back and forth over your abdomen.
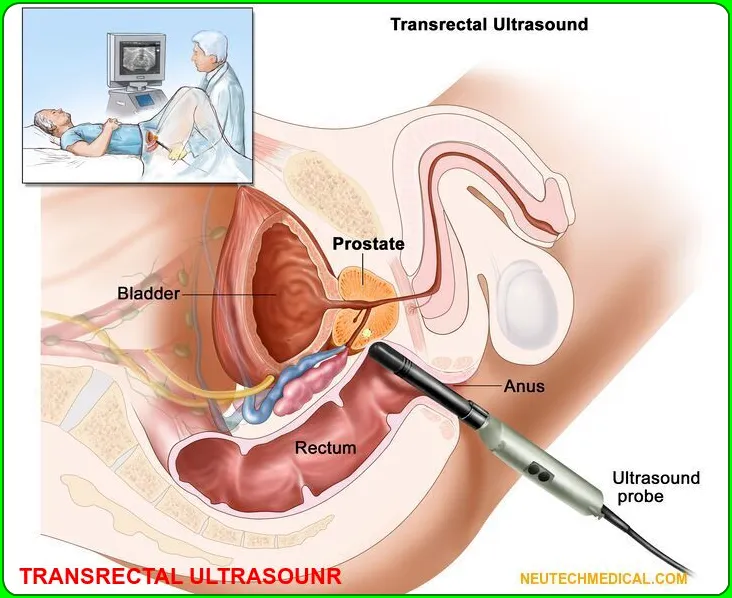
4. Transrectal ultrasound
Transrectal ultrasound is used to look for abnormalities and disturbances in the rectum and nearby structures, including the prostate.
It is also called endorectal ultrasound, ERUS, and TRUS. Transrectal ultrasound. An ultrasound probe is performed in the rectum to examine the prostate.
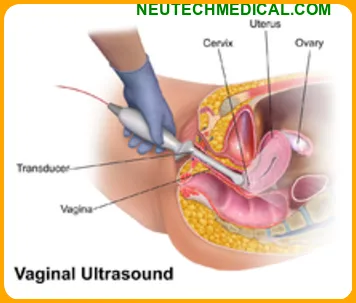
5.Transvaginal ultrasound
In this technique the ultrasound technician or doctor examines the vagina. It may be mildly uncomfortable, but won’t hurt.
The probe is covered with a condom and a gel. The probe transmits sound waves and records the reflections of those waves from the structures of the body. Transabdominal Ultrasound
6. Obstetric Ultrasound
Obstetric ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of a baby (embryo or fetus) as well as the mother’s uterus and ovaries within a pregnant woman. It does not use ionizing radiation, its
There are no known harmful effects yet, and is the preferred method for monitoring pregnant women and their unborn babies. Obstetric Ultrasound
7. Why would a doctor order an ultrasounds of the carotid artery?
Carotid ultrasound is used to test for narrowed carotid arteries, which can lead to stroke.
The danger of coming increases. The carotid arteries are usually narrowed by a buildup of plaque – which is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium and other substances that circulate in the bloodstream.
8. How is a Hysterosonography performed?
Hysterosonography uses sound waves to make pictures of the inside of a woman’s uterus and helps diagnose unexplained vaginal bleeding.
And this involves inserting the transducer into the vagina after you empty your bladder. Hysterosonography is done like a gynecological exam.
9. Pelvic Ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasounds are a non-invasive diagnostic that produces images that are used to assess organs and structures within a woman’s body.
A pelvic ultrasound allows quick visualization of the female pelvic organs and structures including the uterus, cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes and ovaries
10. Renal Ultrasounds
This kidney ultrasounds (renal ultrasound) is an imaging test that allows your healthcare provider to view your right and left kidneys, as well as your bladder.
The kidneys are an important filtration system in your body. They filter waste products from your blood. The waste products then leave your body as urine.
11. What is a thyroid ultrasounds looking for?
Thyroid ultrasound is a sound wave picture of the thyroid gland that is taken by a hand-held device and translated into a 2-dimensional picture on a monitor.
It is used to diagnose tumors, cysts, or goiters of the thyroid, and is a painless, non-risky procedure.
12. What will a testicular ultrasounds show?
The images from the test help them detect patterns that indicate cancer. They can also tell if you have a cyst (fluid-filled sac), a bulge, or a torsion. An ultrasound is also used to diagnose testicular cancer or problems with blood flow to the scrotum.
13. Pediatric Ultrasounds
Why babies might need an ultrasound exam Sometimes, doctors need to look inside babies’ bodies to learn how to help them.
They may use ultrasound to look at different parts of the baby’s abdomen or neck, so they can know why the baby is not feeling well. Ultrasounds can also show doctors how the baby is moving.

Type of Probes use in Ultrasounds
Ultrasound probes come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the part of the body being examined. Some common types of probes include:
a. Linear probes: Used to examine the length of the body, such as the length of the baby in the womb.
b. Sector probes: Used to examine a specific area in more detail, such as the heart.
c. Endoscopic probes: Used to examine internal organs, such as the liver or kidneys.
d. Fetal scalp electrodes: Used to monitor the baby’s heart rate and other vital signs.

Different modes of Ultrasounds
There are many different modes of ultrasound. Some of the more common modes are:
A-mode:- (Amplitude mode – 1D) / What is an A-mode ultrasound? It is the first generation that is used very rarely A-mode is the simplest type of ultrasound.
A single transducer scans a line through the body with the echoes marked on the screen as a function of depth. Therapeutic ultrasound aimed at a specific tumor or calculus is also A-mode, allowing precise focusing of destructive wave energy.
B-mode:- This is the most common mode and is used to create a two-dimensional image of the target.
M-mode:- This mode is used to track movement of objects over time and can be used to measure heart rate and other cardiac functions.
Doppler mode:- This mode is used to measure blood flow and velocity.
CW mode:- In medical imaging systems, Continuous Wave (CW) Doppler is used to measure the blood flow inside the human body.
The ultrasound probe is placed against the patient’s skin and moved across the surface to create the image.
The movement of the probe is generally smooth and consistent, but there may be some areas where the image is distorted. This is usually due to the presence of bone or air in the way of the ultrasound beam.
Standard working processor of ultrasounds
The most common type of ultrasound machine uses a transducer that is placed directly on the skin.
This transducer emits sound waves and then captures the echoes as they bounce off of internal organs and tissues. A computer then uses these echoes to create an image of the inside of the body.
A standard ultrasound machine uses a transducer that is placed on the skin. This transducer emits sound waves and then captures the echoes as they bounce off of internal organs and tissues.
A computer then uses these echoes to create an image of the inside of the body. This type of ultrasound machine is called a “standard” ultrasound machine.
what is the ultrasound cost
The cost of doing USG for a full stomach ranges from $20 to $50. It may be different in different cities.
What is the ultrasound?

An ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture (also known as a sonogram) of organs, tissues, and other structures inside the body.
What is the main use of ultrasound?

An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to make an image of a person’s internal body structures. Doctors commonly use ultrasound to study a developing fetus (unborn baby), a person’s abdominal and pelvic organs, muscles and tendons, or their heart and blood vessels.
What are 3 uses of ultrasound?
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It helps diagnose the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body’s internal organs and to examine an unborn child (fetus) in pregnant women. In infants, doctors commonly use ultrasound to evaluate the brain, hips, and spine.
How is ultrasound done?

During an ultrasound, a healthcare provider passes a device called a transducer or probe over an area of your body or inside a body opening. The provider applies a thin layer of gel to your skin so that the ultrasound waves are transmitted from the transducer through the gel and into your body.
Why is it called ultrasound?
Ultrasound is sound that travels through soft tissue and fluids, but it bounces back, or echoes, off denser surfaces. This is how it creates an image. The term “ultrasound” refers to sound with a frequency that humans cannot hear.
How many types of ultrasound are there?
There are external, internal and endoscopic ultrasound scans. An external ultrasound involves the use of a an ultrasonic sensor also known as a transducer or transceiver which is placed on the patients skin and is moved over the body part being examined.
What are 10 uses of ultrasound?

Ultrasound Definition.
Ultrasound Application:Cleaning.
Ultrasound Application:Detection of Cracks.
Ultrasound Application:Echocardiography.
Ultrasound Application:Ultrasonography.
Ultrasound Application:Lithotripsy.
Ultrasound Application:SONAR.
Ultrasound Application:Echolocation.
What is the range of ultrasound?

2 to 18 megahertz
In physics the term “ultrasound” applies to all acoustic energy with a frequency above human hearing (20,000 hertz or 20 kilohertz). Typical diagnostic sonographic scanners operate in the frequency range of 2 to 18 megahertz, hundreds of times greater than the limit of human hearing.