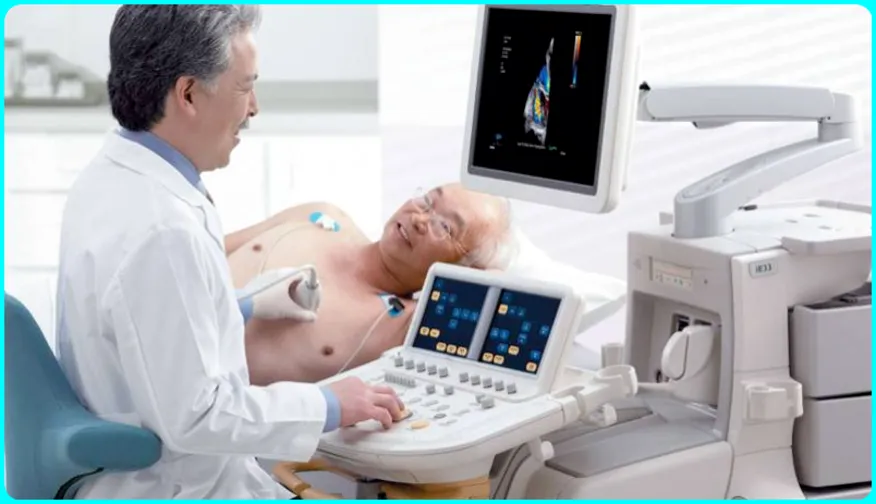
What is an echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram, or more commonly called an echo, shows a graphical outline of your heart rate. In this echo test, your doctor uses high-frequency sound waves to take pictures of your heart’s valves and chambers. This helps the doctor evaluate the pumping function of your heart.
Doctors combine echo with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler techniques to evaluate blood flow to your heart valves. Also, echocardiography does not use radiation. This sets it apart from other tests such as X-rays and CT scans that use a small amount of radiation.
Images can help them get information about:
1.) Knowing the size of the heart, for example, if there is a change in the size, dilation or thickening of the chamber
2.) whether the blood clots in the heart chambers or not
3.) Fluid in the sac around the heart
4.) Having problems with the aorta, which is the main artery connected to the heart
5.) Problems with the pumping function or resting function of the heart
6.) Having problems with the function of the heart valves
7.) Pressure in the heart
An echocardiogram plays an important role in determining the health of the heart muscle, especially after a heart attack. It can also sometimes reveal heart defects, or irregularities, in unborn babies.
Having an echocardiogram is painless. In very rare cases there is a risk with some types of echocardiograms.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:-Sports
What is echocardiography used for?
Echocardiography is a medical imaging technique that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart. It is commonly used for several purposes, including:
- Assessing heart structure and function: Echocardiograms can provide information about the size, shape, and movement of the heart’s chambers, valves, and walls. They help diagnose conditions such as heart muscle abnormalities, valve disorders, and congenital heart defects.
- Evaluating heart function: Echocardiography can measure important parameters like ejection fraction, which indicates how well the heart is pumping blood, and assess the overall function of the heart muscle.
- Detecting heart conditions: It is effective in detecting conditions like heart murmurs, blood clots, fluid buildup around the heart (pericardial effusion), and abnormalities in the heart’s blood vessels.
- Monitoring cardiac health: Echocardiograms can track the progression of heart diseases, monitor the effectiveness of treatments, and assess the recovery after cardiac procedures or surgeries.
- Guiding procedures: During certain interventions, such as cardiac catheterization or heart surgeries, echocardiography provides real-time imaging to guide the placement of instruments and monitor the procedure’s progress.
Echocardiography is a non-invasive and safe procedure, making it a valuable tool in diagnosing and managing various cardiovascular conditions.
1.) an irregular heartbeat
2.) Difficulty in breathing
3.) High or low blood pressure
4.) Swelling of the feet
5.) Abnormal EKG Results
6.) Abnormal sounds between heartbeats
What techniques are used in performing echocardiography?
Several techniques can be used to display pictures of your heart on the display. The best technique depends on your specific situation and what your doctor wants to see. These include the following techniques:
Two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound:- This procedure is most often used. It produces 2D images that appear as “slices” on a computer screen or monitor display. Traditionally, these slices can be “stacked” to form a 3D structure.
Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound:- Advances in technology have made 3D imaging more efficient and useful. New 3-D technologies help doctors understand different aspects of your heart, including how well it pumps blood. Using 3D your doctor can see parts of your heart from different angles.
Doppler ultrasound:- This technique shows how fast your blood is flowing, and in which direction it is flowing.
Color Doppler ultrasound:- This technique also shows your blood flow, plus it uses different colors to highlight different directions of flow.
Stress Imaging:- Through this you can see changes in the way your heart muscle moves. It can catch early signs of any heart disease.
Contrast imaging: Your doctor injects a substance called a contrast agent into your veins. The substance is visible in the images and helps to show the details of your heart. Some people experience an allergic reaction to the contrast agent, but these reactions are usually mild.
Echocardiogram Vs Ekg
An echocardiogram and an electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) are two distinct tests used in the evaluation of heart health, but they provide different types of information.
- Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram is a medical imaging test that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. It provides a visual representation of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns. Echocardiograms can help diagnose conditions such as heart muscle abnormalities, valve disorders, congenital heart defects, and assess overall heart function. It is typically performed by a specially trained technician or a cardiac sonographer.
- Electrocardiogram: An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It involves placing electrodes on the skin to detect the electrical signals generated by the heart as it contracts and relaxes. These signals are then displayed as a waveform or a graph. An EKG provides information about the heart’s rate, rhythm, and the presence of any abnormal electrical patterns. It is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and conduction abnormalities. EKGs are often performed by a healthcare provider or a technician.
In summary, an echocardiogram uses ultrasound to create images of the heart’s structure and function, while an EKG measures the electrical activity of the heart. Echocardiograms provide detailed anatomical and functional information about the heart, while EKGs provide information about the heart’s electrical activity and rhythm. Both tests are valuable tools in assessing heart health, and they are often used together to provide a comprehensive evaluation of cardiac function and structure. The specific test or combination of tests recommended depends on the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and clinical indications.
What are the types of echocardiograms?
There are several types of echocardiograms. Each one offers unique benefits in the diagnosis and management of heart disease. There are mainly three types in this.
1.) Transthoracic echocardiogram.
2.) Transesophageal echocardiogram.
3.) Exercise Stress Echocardiogram.
What is a transthoracic echocardiogram?
A transthoracic echocardiogram is a test that uses ultrasound or sound waves to create images of your heart. This is the most common type of echocardiogram. This test helps the doctor see your heart, its four chambers, four heart valves, and nearby blood vessels.
When do I need a transthoracic echocardiogram?
Doctors use a transthoracic echocardiogram in several ways.
1.) Thoroughly assess heart health before or after diagnosis and treatment.
2.) Identify the cause of certain symptoms.
3.) Screen for and diagnose potential medical conditions.

Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:-Sports
A transthoracic echocardiogram can evaluate heart health by:
a.) Check your heart valves thoroughly.
b.) Determining how well your heart is pumping blood.
c.) Measuring blood pressure and how fast blood is flowing through your heart.
d.) Measuring the size and shape of your heart’s chambers.
This test can identify the cause of cardiac symptoms, such as:
1.) Chest pain.
2.) Having edema (swelling).
3.) Abnormal heart sound.
4.) Having shortness of breath (dyspnea).
A transthoracic echocardiogram is useful for the detection, diagnosis or follow-up of specific medical conditions, including:
1.) Aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection.
2.) Blood clots.
3.) Changes in electrocardiogram (ECG) results.
4.) Congenital heart condition.
5.) Stopping of heart beat.
6.) Heart valve disease.
7.) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
8.) Tumor (heart cancer).
Transthoracic echocardiography advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
1) safe
2) Simple Rapid Set-up
3) Ideal for imaging the pericardial space and epicardial structures
4) Image acquisition and interpretation is familiar to all echocardiographers
5) Does not require general anesthesia
Disadvantages
1) Requires additional personnel
2) May come in the way of fluoroscopy and vice versa
3) Poor image quality in older patients
4) Limited resolution of posterior structures
What is a transesophageal echocardiogram?
A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is an important test that uses sound waves to make pictures of your heart. A TEE differs from other tests of an echocardiogram or ultrasound because it takes pictures from within your body, not from outside it.
Your doctor uses a long, thin, flexible tube called an endoscope to carefully guide a small transducer down your throat and esophagus. A transducer is a device that creates sound waves. These sound waves bounce off different areas of your heart and create an echo. The transducer then sends these echoes to a computer that makes them into pictures. These pictures show the structure and function of your heart in great detail.
Your doctor may combine a transesophageal echocardiogram with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler methods. These special techniques show the speed and direction of blood flow through your heart.
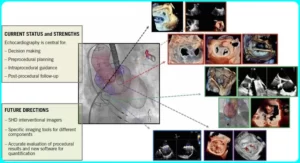
What does a transesophageal echocardiogram show?
A transesophageal echocardiogram gives a detailed view of the structure and function of your heart. It helps in the diagnosis and management of many different conditions including:
1.) Aortic aneurysm, which is a bulge in your largest blood vessel.
2.) Blood clots in your heart People with atrial fibrillation have a higher risk of clots in their atria or upper heart chambers.
3.) Cardiac tumours, which may be cancerous or non-cancerous.
4.) Congenital heart disease, which includes several types of heart problems babies are born with.
5.) Heart valve disease, including mitral valve disease. Your valves may be narrowed or stenosis or leaky. Transesophageal echocardiogram can also detect problems with the prosthetic valve, such as enlargement or infection.
6.) Infectious endocarditis and other infections in the tissues or valves of your heart.
7.) Pericardial disease, which affects the sac that covers your heart.
Why is a transesophageal echocardiogram done?
A transesophageal echocardiogram may be done for several reasons. This mainly includes the following reasons
1.) You had a transthoracic echocardiogram, but your doctor needs a better or more detailed view of your heart. In this case, a TEE is a follow-up to a TTE that can help diagnose or manage a heart problem.
2.) You have a life-threatening problem that needs to be seen by your doctor immediately. TEE can be useful in emergency and critical care.
3.) Your doctor needs to check for blood clots before performing a medical procedure like cardioversion.
4.) You are having a surgery or procedure The TEE helps providers confirm that your surgery was successful. TEEs can also provide real-time imaging during some catheter-based procedures.
Transesophageal echocardiography advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
1) Can be performed simultaneously with fluoroscopy
2) Excellent imaging of posterior structures
Disadvantages
1) Requires general anesthesia
2) Requires special training
3) Requires additional personnel
Intracardiac echocardiography advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
1) does not require general anesthesia
2) Excellent resolution of intracardiac formations and small defects
Disadvantages
1) Time consuming set-up
2) Requires special training
3) Limited reusability of the catheter
4) poor depth penetration
5) need to add
6) Risk of vascular and myocardial damage
What is an exercise stress echocardiogram?
An exercise stress echocardiogram, or echo, is a test that shows how well your heart is working. It uses sound waves to create moving images of your heart. Images of your heart are made. These images allow your doctor to see the size, shape, and movement of your heart and valves.
An exercise stress echo assesses the function of your heart when it is beating rapidly. You create this stress by exercising on a treadmill or bicycle.
It is also commonly called stress echo or echo stress test.
Are there other types of stress tests as well?
Other types of exercise stress tests include:
1.) Exercise Stress Electrocardiogram:- This test is done by using an electrocardiogram to measure the electrical activity of your heart while exercising.
2.) Nuclear exercise stress test:- In this test a small, safe injection of a radioactive substance is injected into your blood vessel which detects special imaging radiation before and after exercise and measures the blood flow to your heart. exposes.
For those who usually can’t exercise, there are two alternative ways to put stress on the heart. Doctors use these methods for stress echocardiograms, EKGs, and nuclear tests.
1.) Pharmacological stress test:- Dobutamine and vasodilators drugs are used to create stress in this test. Dobutamine increases the heart rate. Vasodilators dilate blood vessels thereby increasing blood flow to the heart.
2.) Pacing stress test:- You can get this test done if you have a permanent pacemaker to help stabilize your heart rhythm. Your doctor programs the device to increase your heart rate during a stress test.
When is an echo stress test required?
When doctors often use exercise stress echocardiagrams to diagnose coronary artery disease. This condition occurs when the blood vessels that carry blood to your heart muscle become blocked.
Stress echo can help diagnose or monitor the condition of other conditions
1.) Cardiomyopathy.
2.) Congenital heart disease.
3.) Stopping of heart beat.
4.) Heart valve disease.
5.) High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs.
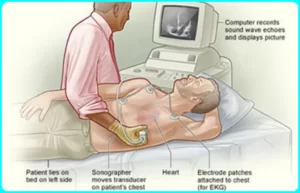
Who should get the stress echo test done?
If someone has symptoms of heart disease, especially if they get worse with activity, they may have this test. These symptoms include:
1.) Chest pain or pressure (angina).
2.) Dizziness or lightheadedness.
3.) Having a fast or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia).
4.) Having shortness of breath (dyspnea).
Other people who may have an exercise stress echocardiogram include:
1.) Athlete.
2.) People who are going to have surgery.
3.) People who are exposed to extreme conditions, such as while diving or at high altitudes.
Who should not get the stress echo test done?
A stress echo may be unsafe if you have some of these heart conditions, such as:
1.) Having aortic dissection.
2.) Inflammation of the tissues in and around the heart, including endocarditis, myocarditis and pericarditis.
3.) Constant pain in the chest.
5.) Have had a recent heart attack.
6.) Severe aortic stenosis.
7.) Uncontrolled arrhythmias.
Who does an exercise stress echocardiogram?
Typically, a cardiac sonographer performs this test under the supervision of a physician. This may happen at your provider’s office or medical center itself.
FAQ
what colors are bad on an echocardiogram?

In an echocardiogram, the colors used to depict blood flow are typically shades of blue and red. These colors are used to represent the direction and speed of blood flow within the heart and blood vessels.
In general, there are no specific “bad” colors on an echocardiogram. The interpretation of colors on an echocardiogram depends on the context and the specific findings being evaluated.
Healthcare professionals who specialize in reading echocardiograms, such as cardiologists or cardiac sonographers, analyze the colors in conjunction with other parameters and clinical information to assess the function and structure of the heart.
what is an echocardiogram vs ekg

an echocardiogram uses ultrasound to create images of the heart’s structure and function, while an EKG measures the electrical activity of the heart. Both tests are valuable tools in evaluating heart health, but they provide complementary information and are often used together to assess cardiac conditions.
what is the difference between an ekg and an echocardiogram

an echocardiogram uses ultrasound to create images of the heart’s structure and function, while an EKG measures the electrical activity of the heart. Both tests are valuable tools in evaluating heart health, but they provide complementary information and are often used together to assess cardiac conditions.
An echocardiogram is a medical imaging test that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. It provides a visual representation of the heart, including its chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns.
Echocardiograms can help diagnose conditions such as heart muscle abnormalities, valve disorders, congenital heart defects, and assess overall heart function. It is typically performed by a specially trained technician or a cardiac sonographer.
what is a transthoracic echocardiogram

A TTE provides valuable information about the structure and function of the heart. It helps assess parameters such as the size and thickness of the heart muscle, the condition of the heart valves, the movement of the heart walls, and the overall pumping function of the heart. It can also evaluate blood flow velocities and detect abnormalities such as blood clots, fluid accumulation, or congenital heart defects.
why do i need a transthoracic echocardiogram
Ultimately, the decision to undergo a TTE is based on a careful evaluation by your healthcare provider, who will consider your medical history, symptoms, and specific clinical indications to determine the most appropriate diagnostic approach. It’s best to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your individual situation and reasons for needing a transthoracic echocardiogram.










