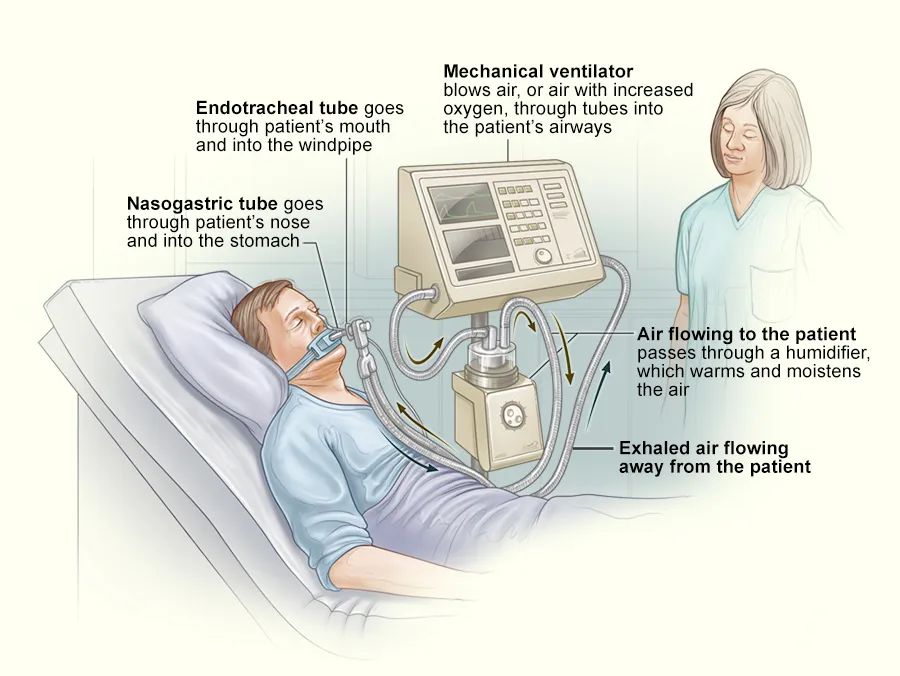
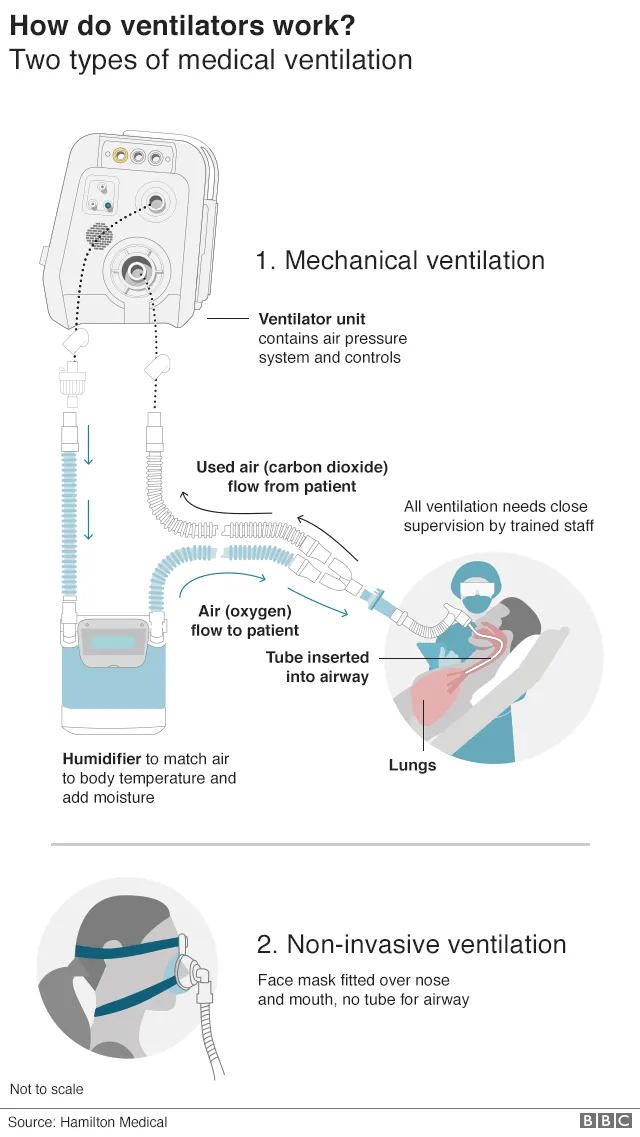
VENTILATOR
Mechanical ventilation is the mode of Operation to ventilate a patient through an external device. Air is pushes into the lungs.
SPONTANEOUS ventilation is a type of breathing that is complete done by the patient without any device’s help. Air is pull into the lungs.
BRIEF INTRODUCTION VENTILATOR
A mechanical ventilator assists breathing and inflate lungs by delivering oxygen-enriched air into the lungs. The ventilator will target either pressure or volume in doing this.
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:-Sports
In spontaneously breathing patients, each breath will triggers by a change in pressure or flow in the circuit. Each inspiration will cycle off by either a time limit or a decrease inflow.
Ventilation is a process by which it allows the breathable air to move in and out of the lungs when the patient is not able to breathe sufficiently.
The flow of air to the lungs is facilitate by generating a negative pressure around the patient’s thoracic cage.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
The Ventilator system works on Boyle’s law which states that ‚for a fixed numbers of molecules at a fixed temperature, the pressure of a gas varies inversely to the volume of gas‛
P=k/V or P1V1=P2V
Ventilation is require when there is an obstruction in the airway of a patient. Here applies
“Poiseuille’s” “law” which states that ‚driving pressure required to maintain same flow in the airway is increase when the radius of airway decreased to half of its original size.
Mathematically,
∆P = Flow/radius^4
Factors that commonly cause breakdown Leaving electromechanical failures-
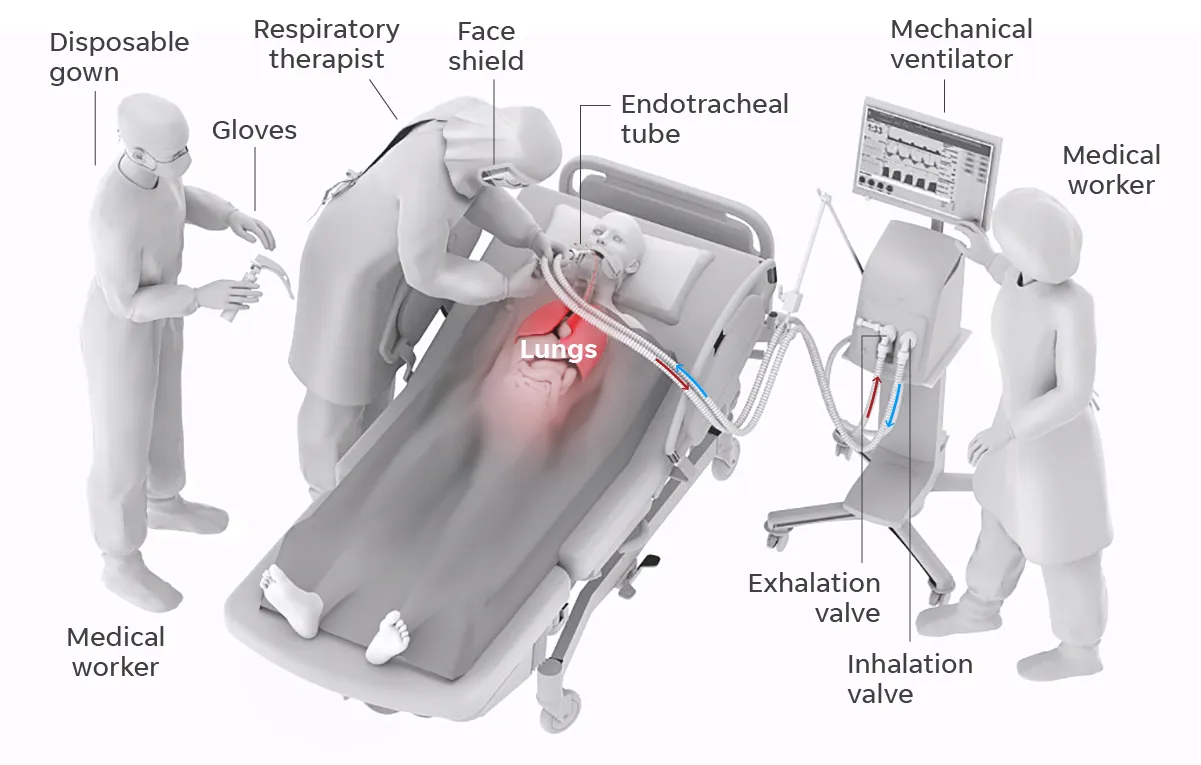
1- Secretions from the patient into respiratory tracts which lead to malfunctioning of flow sensors/expiratory filters.
2- Moisturize in Air & O2 line cause Inspiratory manifold to malfunction.
3- Reuse of disposable parts again & again.
Circumstances in which ventilator is applies At a certain time when the patient is unable to breathe on their own,
the ventilator is applies to a patient as external support for breathing. Applied for the patients for a while post-surgery.
1- Multiple organ failure.
2- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
3- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).
4- Traumatic patients.
5- Other pre-existing respiratory diseases.
Maintenance
1- Clean expiratory valve assembly/ flow sensors carefully (reusable).
2- Clean water trap of Inspiratory manifold in case of heavy moisture in air/O2 line.
3- Check for proper electrical requirements as per guidelines provided in manuals.
Preventive
1- Avoid reusing disposable materials.
2- Check for moisture in central line supplies.
3- Check for pressure level in a central line.
Tidal Volume
A normal amount of gas a person inhales & exhales.
The mechanical ventilator provides Tidal Volume on basis of the weight of the patient which varies as per ‘patient type’
Adult/Pediatric- 8~10 ml/Kg Neonatal- 5-6 ml/Kg
Ventilator Modes
A/CMC- Assist/Controlled Mandatory Ventilation. Used when the patient is unconscious and unable to do breathing SIMV- Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation. when the patient tries to breathe by himself assistance is require by the ventilator to reduce his/her effort of breathing.
Main components of Ventilation
1- Gas Inlet System
2- Gas Mixing System
3- Flow sensors
Motherboard/CPU PCB
Analog PCB
Breathing Circuit Expiratory Manifold
1-Expiratory Filters.
2-Expiratory Valve Assembly.
Power Supply System.
Backup Power Supply System.
Above consists of many other complex sub-systems.
The ventilator works by applying a positive pressure breath and depends on the compliance and resistance of the airway system,
which is affected by how much pressure is generated by the ventilator to provide a given tidal volume (TV) should be done. Tv is the volume of air entering the lungs during inhalation.
A ventilator is an automated machine designed to provide all or part of the body with a way to move gas in and out of the lungs. The process of moving air in and out of the lungs is called breathing, or ventilation.