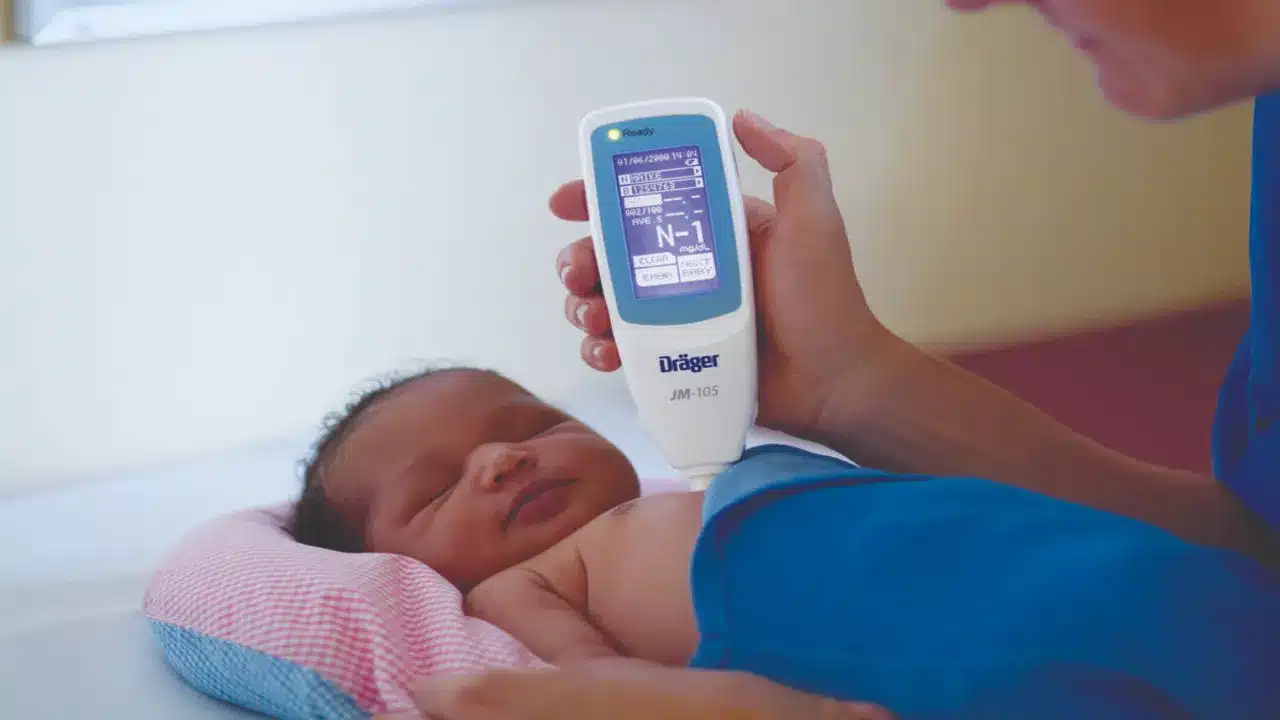

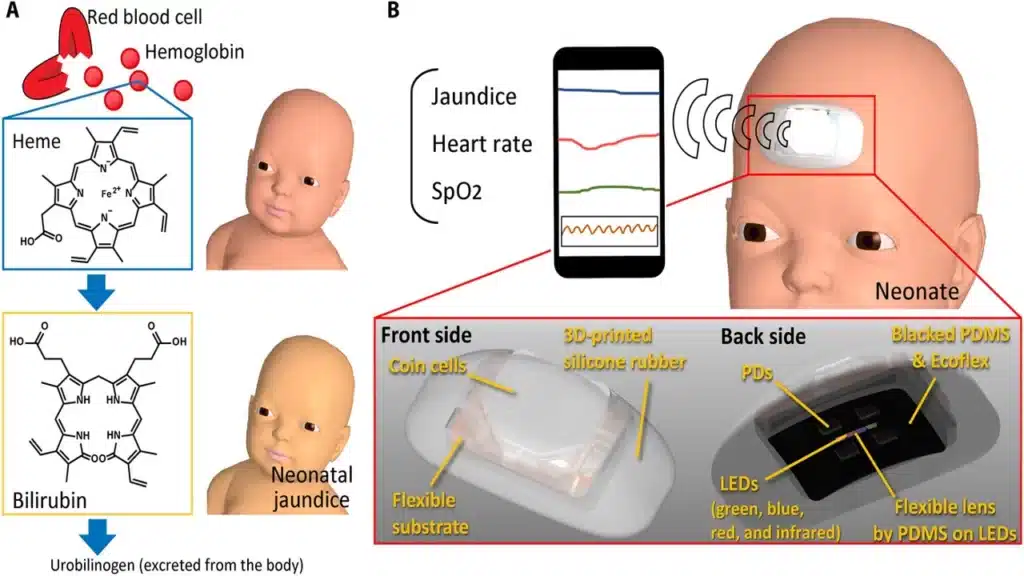
Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer
Jaundice in newborns occurs in about 70% term and 80% in preterm.
Management of jaundiced neonates often requires measurement of total serum bilirubin (TSB).
Total serum bilirubin (TSB) is usually determined by spectrophotometric methods by analyzing plasma or serum samples.
Such techniques require blood to be drawn to cause pain and trauma to the newborn. In addition there is a wide range of intra- and inter-laboratory variability in performance Bilirubin analyzer.
These problems have led to the search for a non-invasive, reliable technique for the assessment of TSB. A transcutaneous bilirubin meter works by directing light into the skin and measuring the intensity of the wavelength of the light coming back.
Transcutaneous bilirubin measurement is a non-invasive method for measuring serum bilirubin levels.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
Working Principle
Bilirubin concentrations are determined either by whole blood or serum analysis using spectrophotometric methods or by skin-reflectance measurements.
The three methods of spectrophotometric analysis are the direct spectrophotometric method, the Malloy-Evelyn method, and the Jendrassik-Grof method.
Categories
(i) Multi-wavelength Spectral Reflectance meters.
(ii) Two-wavelength (460 nm, 540 nm) Spectral Reflectance meters.
(a) Multi-wavelength Spectral Reflectance meters
The major components that provide spectral reflectance in newborns are melanin, dermal maturation, hemoglobin and bilirubin. Most bilirubin meters only analyze certain wavelengths; As a result, dermal maturation and melanin content will interfere with the outcome.
With these meters, separate analysis for each patient population was required. To overcome this problem the multi-reflectance spectral bilirubin meter has been designed.
This instrument performs spectral analysis at more than 100 different wavelengths and by subtracting the spectral combination of known components, bilirubin absorption is quantified. This technique eliminates the need for separate charts for different populations.

(b) Two-wavelength Spectral Reflectance meters
Blood samples are required for spectrophotometric analysis. The analysis technique depends on both the type or types of bilirubin being measured and the age of the patient (newborn or adult).
A light-emitting sensor is placed on the baby’s skin (preferably on the forehead or sternum). The reflected light is split into two beams by a dichroic mirror, and wavelengths of 455 nm and 575 nm are measured by optical detectors.
Transcutaneous bilirubin measurement is a non-invasive method for measuring serum bilirubin levels.
Transcutaneous bilirubinometer works by directing light into the skin and measuring the intensity of the wavelength of the light coming back. Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer
Transcutaneous bilirubin devices that estimate the amount of serum bilirubin have been found non-invasively to reduce the need for blood from newborns.
The meter analyzes the spectrum of the optical signal reflected from the subcutaneous tissue of the newborn.
These optical signals are converted into electrical signals by a photocell. These are analyzed by a microprocessor to determine the amount of serum bilirubin.
A bilirubin-meter is an instrument designed to determine the amount of bilirubin in blood or other clinical specimen. Aims to facilitate easy and quick assessment of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns. Most newborns with jaundice should continue to breastfeed.
Breastfeeding more often improves a mother’s milk supply and, in turn, may improve the infant’s caloric intake and hydration, thus reducing elevated bilirubin.
Transcutaneous bilirubin meters, although not as accurate as measuring serum bilirubin, are more accurate than visual inspection alone, are non-invasive, can be used in the community, and provide immediate results.

The accuracy of using TCB values to detect newborns requiring phototherapy is 92.5%. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) are 78.3, 94.2, 62.1, and 97.3%, respectively.
Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer Price
The price of a transcutaneous bilirubinometer can vary depending on various factors such as brand, model, features, and where you buy it. Typically, the cost of a transcutaneous bilirubinometer ranges from about $500 to $3,000 or more.
It is worth noting that the prices mentioned above are approximate and can vary greatly. To get accurate pricing information, it is best to check with medical device suppliers, online marketplaces, or contact manufacturers directly. Additionally, prices may vary between countries and regions, so it is advised to check the local market for the most up-to-date pricing information.

How to use Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer
Using a transcutaneous bilirubinometer usually involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Make sure the infant is calm, cool, and comfortable. Remove any clothing or objects that may obstruct reading.
- Positioning: Place the infant in the supine position (lay on their back) and place the skin over the sternum or forehead. The exact location may vary depending on the device and manufacturer’s instructions.
- Calibration: Turn on the bilirubinometer and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration if necessary. This step may involve setting the device to the appropriate age or weight of the baby.
- Measurement: Place the device’s sensor on an exposed skin area (sternum or forehead) and ensure good contact. The device will emit light onto the skin and measure the reflected or transmitted light to estimate bilirubin levels.
- Reading: Wait for the device to analyze the measurement and display the bilirubin level. The result is usually shown as a numerical value in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or micromole per liter (µmol/L).
- RECORD AND INTERPRET: Record the bilirubin level in the infant’s medical record. Compare the reading with the appropriate reference range or chart provided by the manufacturer or medical guidelines to interpret the result.
- Follow-up: If bilirubin levels are elevated or concerning, consult a health care professional for further evaluation and management. They may recommend additional tests or interventions as needed.
Remember to consult the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer of your transcutaneous bilirubinometer, as there may be slight variations in the operation and use of different devices.
Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer Normal Range
The normal range for transcutaneous bilirubin levels may vary depending on the device and the age of the infant. However, as a general guideline, the normal range for transcutaneous bilirubin levels in healthy term infants is generally considered to be less than 12 mg/dL or less than 205 µmol/L.
It is important to note that these values may vary slightly between different instruments and populations, and bilirubin levels should always be interpreted in the context of the infant’s age, clinical presentation, and any additional risk factors.
It is recommended to consult the specific reference range provided by the manufacturer of your transcutaneous bilirubinometer or follow the guidelines and protocols established by your healthcare facility or medical professional for accurate interpretation of bilirubin levels.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
Best Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer
The concept of “best” may vary depending on specific needs and preferences. However, I can provide you with a list of popular and well regarded transcutaneous bilirubinometers that are commonly used in clinical settings. It is important to note that the suitability of a specific device may depend on factors such as budget, facilities, availability, and compatibility with your healthcare facility’s protocols. Some popular transcutaneous bilirubinometers include:
When evaluating a transcutaneous bilirubinometer, consider factors such as:
- Accuracy: Look for devices that have been clinically validated and provide accurate measurements. Check for any validation studies or certifications.
- Ease of use: Consider the tools user-friendly with clear instructions and intuitive interfaces.
- Reliability: Look for instruments known for consistent and reliable readings.
- Data Management: Consider tools that offer convenient data storage and management options.
- Cost: Evaluate the cost of the device with respect to its features and your budget.
- Customer Reviews: Read reviews and opinions from healthcare professionals and other users to gather insight on the performance and satisfaction of various devices.
Based on these features, we have given some good products.
- BiliCheck Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer by Philips Healthcare
- JM-105 Jaundice Meter by Dräger
- JM-103 Jaundice Meter by Dräger
- BiliCheck Plus Transcutaneous Bilirubin Analyzer by Respironics
- BiliCare LED Transcutaneous Jaundice Meter by Medica
When selecting a transcutaneous bilirubinometer, it is recommended to consult with healthcare professionals or medical device suppliers who can provide more specific guidance based on your needs and available options. Additionally, reading product reviews and comparing features and prices can help you make an informed decision.
FAQ
What is a transcutaneous bilirubinometer

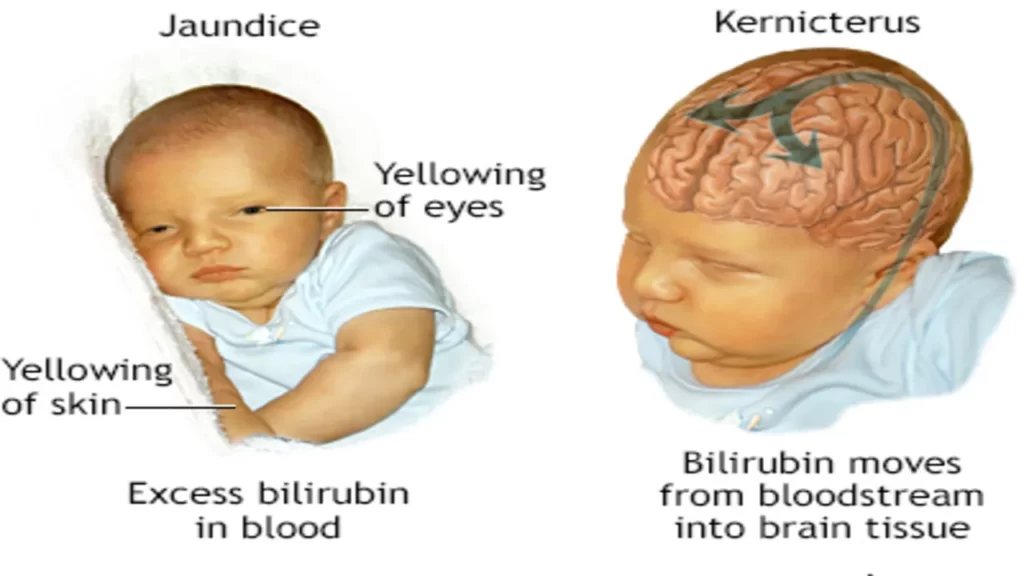
A transcutaneous bilirubinometer is a medical device used to measure the level of bilirubin in a patient’s blood without the need for a blood sample. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is produced when red blood cells break down. Elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood can indicate a variety of conditions, including jaundice, a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes.
What part if body to use transcutaneous bilirubinometer

Transcutaneous bilirubinometers can be used on various parts of the body to measure bilirubin levels. The specific location may vary depending on the device and manufacturer’s instructions. However, the most commonly used areas for transcutaneous bilirubinometry are the head and sternum (chest) and the forehead.
How does transcutaneous bilirubinometer work

Transcutaneous bilirubinometers work by using light to estimate the level of bilirubin in a patient’s blood without the need for a blood sample. These instruments use the principle of photometry to measure the absorption, reflection or transmission of light.
Light Emission: The device emits light of a specific wavelength onto the patient’s skin. The wavelengths used are typically in the range of 460 to 500 nanometers.
Light interaction with tissue. …
Light Detection. …
data analysis. …
Bilirubin estimation. …




