
What is the Thyroid Ultrasound Purpose
Thyroid ultrasonography is the process of imaging the thyroid gland using sound waves using a handheld device and converting the image to a two-dimensional display on a monitor. It is a painless, risk-free treatment used to diagnose thyroid cancers, cysts, or goiters.
A thyroid ultrasound is a medical imaging procedure that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the thyroid gland, which is located in the front of the neck. The purpose of a thyroid ultrasound is to assess the structure and condition of the thyroid gland. Here are some specific purposes for which a thyroid ultrasound may be performed:
- Detecting Abnormalities:
- Nodules: Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths or lumps in the thyroid tissue. A thyroid ultrasound can help identify the presence, size, and characteristics of these nodules.
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs, known as cysts, can sometimes form in the thyroid. Ultrasound helps in visualizing and characterizing these cystic structures.
- Evaluating Thyroid Size:
- The ultrasound can measure the size of the thyroid gland and detect any enlargement (goiter) or atrophy.
- Assessing Blood Flow:
- Doppler ultrasound, a technique that evaluates blood flow, can be used to assess the vascularity of the thyroid gland. This is particularly useful in differentiating between benign and malignant nodules.
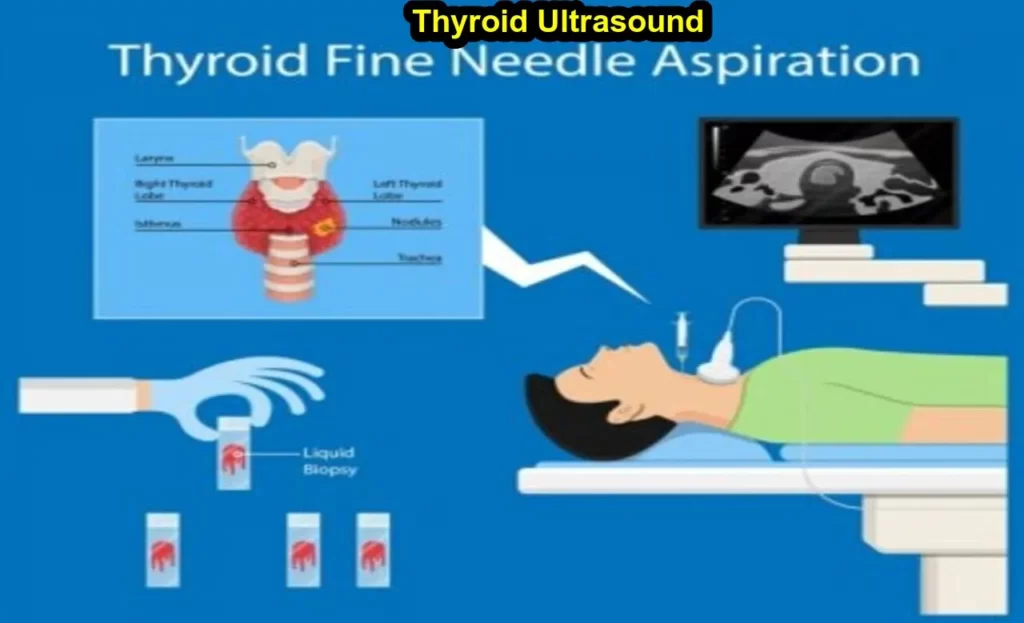
- Guiding Biopsy Procedures:
- If a suspicious nodule is identified, a fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample for further analysis. Ultrasound guidance is often used to ensure accurate targeting of the biopsy needle.
- Monitoring Thyroid Disorders:
- Individuals with thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease, may undergo thyroid ultrasound to monitor changes in the gland over time.
- Differentiating Between Types of Thyroid Lesions:
- Ultrasound imaging helps distinguish between solid nodules, cystic nodules, or a combination of both. Solid nodules may be more concerning and require further evaluation.
- Evaluating Thyroid Function:
- While thyroid ultrasound itself does not assess thyroid function directly, it provides valuable information about the gland’s structure, which can complement other diagnostic tests for a comprehensive evaluation of thyroid health.
- Preoperative Assessment:
- In cases where thyroid surgery (thyroidectomy) is planned, a preoperative ultrasound can provide valuable information about the size and location of thyroid nodules and guide the surgeon in planning the procedure.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports

During the procedure, you will lie on your back with your head turned to one side. A gel will be applied to your skin, and a small device called a transducer will be placed on your neck. The transducer emits sound waves that create images of your thyroid gland on a computer screen.
Thyroid Ultrasound
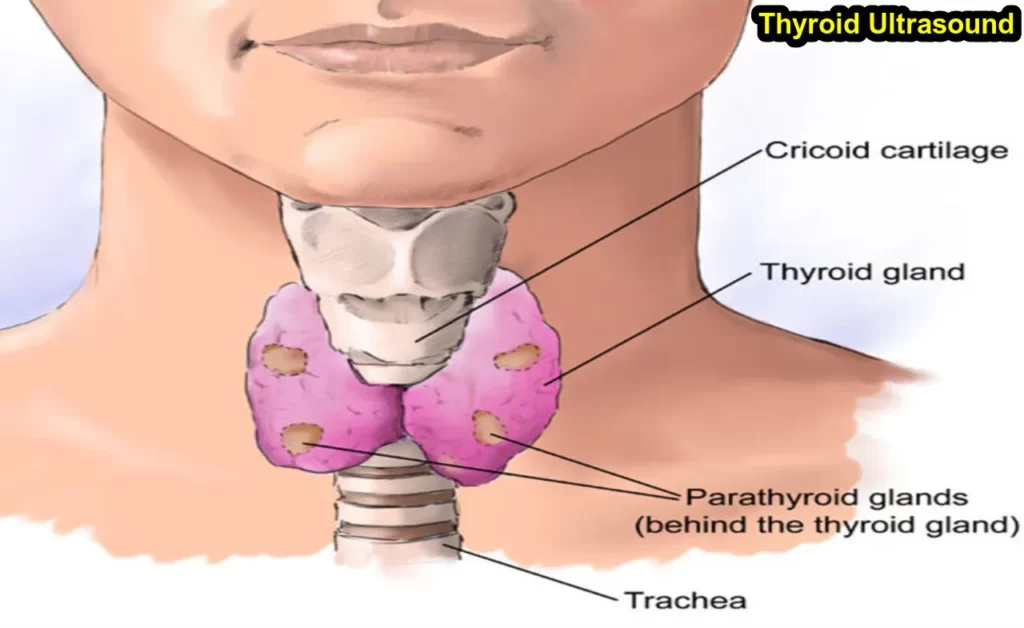
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck that produces hormones that control the body’s metabolism. Thyroid ultrasound is used to evaluate the size, shape, and appearance of the gland. It can also help assess blood flow to the gland and detect abnormal growth.
The procedure is usually performed in an outpatient setting by a radiologist or sonographer. The patient will be asked to lie on their back with their head turned to one side. A gel will be applied to the skin over the area being tested and a transducer (hand held device) will be placed on the skin. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off structures inside the body and are captured by a computer, which creates images of the internal structures.
This test requires no preparation and is generally well tolerated by patients. After the procedure, patients can resume their normal activities immediately. There are no known risks or side effects associated with thyroid ultrasound.
If an abnormal growth is detected on a thyroid ultrasound, further testing may be recommended to confirm the findings and determine if treatment is necessary.

Nodules on Thyroid Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a sound wave that is higher in frequency than can be detected by the human ear. It is used to create images of structures within the body. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland normally located in the lower part of the neck. The gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism.
Nodules on thyroid ultrasound are abnormal growths of thyroid tissue that may be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). They are usually found during a routine ultrasound exam of the neck.
Most thyroid nodules are benign and cause no symptoms. However, if the nodule is large enough, it can cause problems such as difficulty swallowing or breathing. Malignant masses can grow rapidly and spread to other parts of the body.
If a nodule is found on thyroide ultrasound, further testing may be needed to determine whether it is benign or malignant. This may include a fine needle aspiration biopsy, in which a needle is used to remove cells from the nodule for laboratory analysis.
Abnormal Thyroid Ultrasound
An abnormal thyroid ultrasound can be caused by a number of things, including:
- Enlargement or mass in the thyroid gland
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Abnormalities in the blood vessels around the thyroid gland
If your doctor suspects that you have an abnormal thyroid ultrasound, they will order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for an abnormal thyroid ultrasound will depend on the underlying cause.
Thyroid Cancer Normal vs Abnormal Thyroid Ultrasound
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the lower part of the neck. The main purpose of thyroid ultrasound is to evaluate the size, shape and texture of the gland.
Thyroid cancer is the most common type of cancer that develops in the thyroid gland. Most cases of thyroid cancer can be diagnosed using ultrasound. Thyroid cancer usually presents as a mass or lump in the thyroid gland. Ultrasound can help determine whether a mass is benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Abnormalities in the size, shape, or texture of the thyroid gland may be a sign of thyroid cancer. An abnormal ultrasound may show a mass that is larger than normal, has irregular borders, and/or has an abnormal texture. If you have any concerns about your thyroide ultrasound results, be sure to discuss them with your doctor.
Thyroid Ultrasound Hashimoto’s
Thyroid ultrasound is a medical procedure used to assess the health of the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the front of the neck. The gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. The sound waves are directed at the thyroid gland and bounce off it. The bouncing sound waves are then converted into electrical signals that are displayed as images on a computer screen.
The purpose of thyroid ultrasound is to evaluate the size, shape, and consistency of the gland. The procedure may also be used to detect abnormalities such as lumps or masses. A thyroid ultrasound is often used to diagnose conditions such as Hashimoto’s disease, Graves’ disease, and goiter.
Thyroid ultrasound is usually a safe and painless procedure. There is no radiation risk associated with this type of imaging. Some people may experience mild discomfort from lying on their back for long periods of time or straining their neck during the test.
If you are scheduled for a thyroid ultrasound, you should wear loose-fitting clothing so that your neck and upper chest area is accessible for the exam. You will be asked to lie on your back on an examination table.
FAQ
What is the cost of thyroid scan?
Thyroid Scan Test Price in Delhi typically ranges from INR 3000 to INR 4000, depending on the diagnostic center.
Can a thyroid ultrasound detect cancer?

In most cases, an excellent thyroid ultrasound is sufficient to make the diagnosis of thyroid cancer since some thyroid cancers have very characteristic ultrasound appearances.
Why would a doctor recommend a thyroid ultrasound?

When physical examination shows any of these findings, a thyroid ultrasound is usually recommended: You have a growth on your thyroid gland, called a thyroid nodule. The thyroid feels big or irregular, called a goiter. You have abnormal lymph nodes near your thyroid gland.
What does an ultrasound of your thyroid show?

Nodules that are solid or filled with fluid can be determined using thyroid ultrasound. (Solid nodules are more likely to be cancerous.) This test can also be used to check the number and size of thyroid nodules as well as reveal how their blood supply looks.
Who needs thyroid ultrasound?

When the thyroid gland feels large or irregular, called a goiter, or when abnormal lymph nodes surround the thyroid, a thyroid ultrasound is usually recommended.
Can I eat before thyroid ultrasound?
Put on loose, comfortable attire that reveals your neck so the doctor or ultrasonographer may inspect it more readily. Turtlenecks and other items of clothing with collars are a few examples of what might make the ultrasound examination challenging. There is no need for you to adjust your medication or diet in preparation for this assessment.
Who needs a thyroid scan?
Thyroid uptake is measured in order to assess gland function. Those who have thyroid cancer or have had it in the past usually receive a whole-body thyroid scan. These imaging tests can be carried out by a doctor to: ascertain whether the gland is functioning normally.









