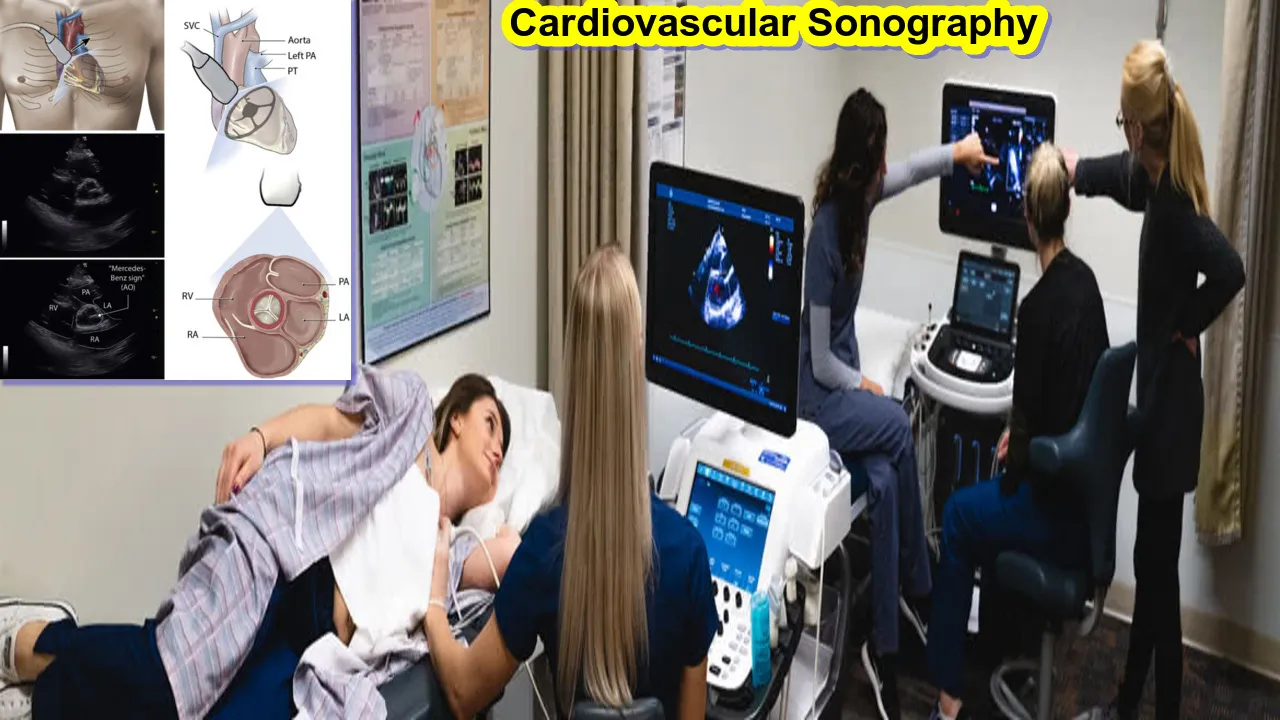
What is Cardiovascular Sonography
Echocardiography, another name for cardiovascular sonography, is a type of medical imaging that employs ultrasonography to provide finely detailed pictures of the heart and its surrounding tissues. This non-invasive diagnostic device is essential for evaluating the anatomy and physiology of the heart, yielding important data for the identification and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Key Aspects of Cardiovascular Sonography:
- Ultrasound Waves:
- Similar to general ultrasound, cardiovascular sonography relies on high-frequency sound waves that are emitted from a transducer. These sound waves travel through the chest, and their reflections create detailed images of the heart in real time.
- Transducer Placement:
- The transducer, a handheld device, is typically placed on the chest wall, allowing for the visualization of the heart and its chambers from various angles. In some cases, a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) may be performed, where the transducer is passed into the esophagus to obtain clearer images.
- Image Types:
- Cardiovascular sonography produces different types of images, including two-dimensional (2D) images that provide a detailed view of the heart’s structures, as well as Doppler and color Doppler images that visualize blood flow within the heart and blood vessels.
- Evaluating Heart Function:
- Cardiovascular sonography allows healthcare professionals to assess the size, shape, and movement of the heart’s chambers and valves. It provides information about the heart’s pumping function, helping to identify abnormalities such as cardiomyopathies or heart valve disorders.
- Detecting Heart Conditions:
- This imaging technique is commonly used to diagnose a variety of cardiovascular conditions, including:
- Valve abnormalities: Assessing conditions like stenosis or regurgitation.
- Congenital heart defects: Identifying structural abnormalities present from birth.
- Cardiac tumors: Detecting any unusual growths within the heart.
- Cardiac infections: Identifying inflammation or infections affecting the heart.
- This imaging technique is commonly used to diagnose a variety of cardiovascular conditions, including:
- Guidance for Interventions:
- Cardiovascular sonography is often used to guide interventional procedures, such as heart catheterizations or surgical interventions. It provides real-time imaging to assist in navigating and monitoring these procedures.
- Monitoring Progress:
- Follow-up echocardiograms can be performed to monitor the progress of treatment or the recovery of a patient with a cardiovascular condition.
Cardiovascular Sonography
Cardiovascular sonography, also known as echocardiography or cardiac ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the heart. Cardiovascular sonographers work closely with cardiologists and other medical professionals to provide information about the structure and function of the heart.
The field of cardiovasculars sonography is constantly evolving, and new technology is always being developed to improve image quality and diagnostic accuracy. As a result, cardiovascular sonographers must be lifelong learners, keeping up with the latest advancements in their field.
Cardiovascular sonographers typically work in hospitals, clinics, or private practices. They may also work in research settings or be employed by companies that manufacture cardiac ultrasound equipment.
Most cardiovascular sonographers hold at least an Associate’s degree in cardiovascular sonography from an accredited program. Some also hold a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree. certification from the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) is also required for many positions in the field.
Cardiovascular sonographers are in high demand, and the job outlook for this career is very positive. The median annual salary for cardiovascular sonographers was $68,530 in 2017, and jobs in this field are expected to grow much faster than average over the next decade.
How to Use cardiovascular sonography
To produce clear and reliable pictures of the heart and its structures, various measures must be taken while using cardiovascular sonography, also known as echocardiography. This is a broad overview of the procedures often used in cardiovascular sonography:
- Patient Preparation:
- Explain the procedure to the patient, including its purpose and what to expect.
- Ensure the patient is in a suitable position, usually lying on their back, and expose the chest area.
- Attach Electrodes (ECG Leads):
- Attach electrocardiogram (ECG) electrodes to the patient’s chest. This helps synchronize the cardiac cycle with the ultrasound images, providing a clearer picture of the heart’s structures.
- Apply Ultrasound Gel:
- Apply a water-based ultrasound gel to the patient’s chest. This gel facilitates the transmission of ultrasound waves and improves the quality of the images.
- Position the Transducer:
- Place the ultrasound transducer on the chest in various positions to visualize different angles of the heart. The transducer emits and receives sound waves, creating real-time images on the monitor.
- Adjust Settings:
- Use the ultrasound machine’s control panel to adjust settings such as depth, frequency, and gain. These settings help optimize the images for better visualization of cardiac structures.
- Obtain Standard Views:
- Acquire standard views of the heart, including the parasternal, apical, and subcostal views. Each view provides specific information about the heart’s chambers, valves, and overall function.
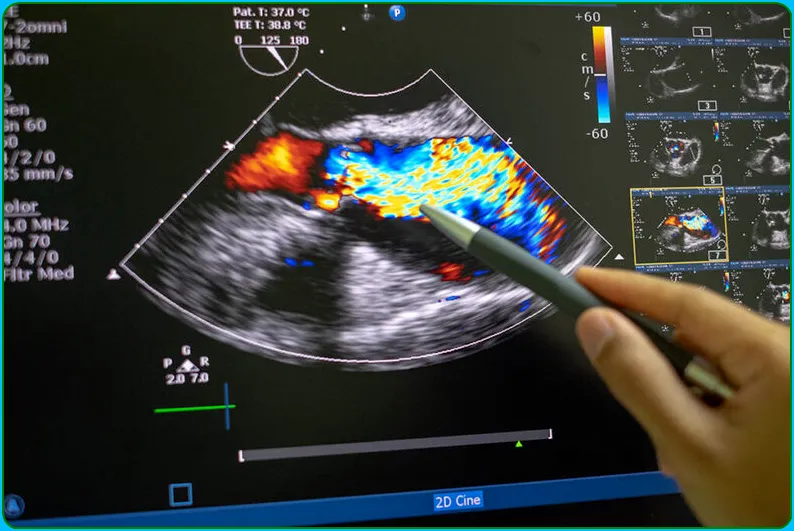
- Doppler and Color Doppler Imaging:
- Utilize Doppler and color Doppler imaging modes to assess blood flow within the heart and blood vessels. Doppler allows for the evaluation of the speed and direction of blood flow, helping to detect abnormalities like valve regurgitation or stenosis.
- Measurements and Analysis:
- Take measurements of various cardiac parameters, such as chamber dimensions, wall thickness, and ejection fraction. This quantitative data aids in the assessment of cardiac function.
- Record and Save Images:
- Record relevant portions of the examination by freezing frames or capturing specific images. Some machines also allow for the storage and archiving of images for future reference.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (if needed):
- If a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is required for clearer images, the transducer may be inserted into the patient’s esophagus after the patient is sedated. This is typically done for specific diagnostic purposes.
- Conclude the Examination:
- Once the necessary images and data have been obtained, conclude the examination. Wipe off the ultrasound gel from the patient’s chest.
- Interpretation and Reporting:
- The obtained images are interpreted by a healthcare professional, often a cardiologist, who generates a report based on the findings. This report helps guide further diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Cardiovascular Sonography
Cardiovascular sonography involves the use of a transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the structures of the heart to produce echoes. These echoes are then converted into real-time images using advanced computer technology. The resulting images provide valuable information about the heart’s chambers, valves, blood flow, and overall heart function.
Clinical Applications of Cardiovascular Sonography
Cardiac sonography plays an important role in the diagnosis of a variety of heart conditions. By obtaining detailed images of the heart, sonographers and cardiologists can identify abnormalities and assess heart function. Some of the more common conditions diagnosed through cardiovascular sonography include:
- Congenital Heart Defects:- Congenital heart defects are structural abnormalities present at birth. Cardiovascular sonography allows health professionals to evaluate the structure of the heart and identify any defects. This information helps guide treatment decisions and surgical interventions if necessary.
- Coronary Artery Disease:- Cardiovascular sonography can assess the health of the coronary arteries and detect any blockages caused by plaque buildup. By observing blood flow in the coronary arteries, sonographers can identify areas with reduced blood supply, helping physicians determine appropriate treatment options.
- Valvular Heart Disease:- Sonography enables evaluation of the heart valves and the detection of abnormalities such as valve stenosis or regurgitation. Accurate assessment of valvular function helps cardiologists determine the need for intervention such as valve repair or replacement.
- Cardiomyopathy:- Cardiomyopathies are diseases that affect the heart muscle, causing structural and functional abnormalities. Cardiovascular sonography helps diagnose the different types of cardiomyopathy, guide treatment plans, and monitor disease progression.
Role in guiding cardiac interventions
Apart from diagnosis, cardiac sonography also plays an important role in guiding various cardiac interventions. By providing real-time images, sonographers assist physicians during the following procedures:
- Echocardiogram-Guided Biopsy:- In cases where a cardiac biopsy is necessary, sonography helps guide the precise placement of the biopsy needle. This ensures that the sample obtained is representative of the affected area, thereby aiding in the diagnosis of heart diseases.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE):- TEE involves inserting a special transducer into the esophagus to obtain detailed images of the heart’s structures. It is especially useful in assessing heart valves, detecting blood clots, and evaluating patients with complex heart conditions.
- Intraoperative Echocardiography:- During cardiac surgery, sonographers provide real-time imaging to guide surgeons, allowing them to visualize the structures of the heart and monitor any changes during the procedure. This helps ensure the success and safety of the surgery.

What is Cardiovascular Sonography Program
There are many great cardiovascular sonography programs available today. The best way to find one that is right for you is to research the different options and then make a decision based on your specific needs and goals.
When looking at programs, you will want to consider things like cost, length of time required to complete the program, accreditation, and job placement assistance. Make sure you choose a program that is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Joint Review Committee on Education in Diagnostic Medical Sonography (JRCDMS).
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
Different types of cardiovascular sonography
Cardiovascular sonography is the term for a group of imaging methods used to see the heart and its associated components. These methods give special insights into the cardiovascular system and are applied for various therapeutic applications. Key varieties of cardiovascular sonography include the following:
- Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE):
- This is the most common form of echocardiography. TTE involves placing the ultrasound transducer on the patient’s chest to obtain images of the heart through the chest wall. It provides valuable information about the heart’s chambers, valves, and overall function.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE):
- TEE involves inserting a specialized ultrasound transducer into the esophagus, located behind the heart. This closer proximity allows for clearer and more detailed images, especially of the posterior heart structures. TEE is often used for detailed assessment of cardiac valves, the aorta, and the atria.
- Stress Echocardiography:
- Stress echocardiography combines echocardiography with physical or pharmacological stress to evaluate how the heart performs under increased workload. This can help identify areas of the heart that may not be receiving enough blood, indicating potential coronary artery disease.
- Doppler Echocardiography:
- Doppler echocardiography measures the speed and direction of blood flow within the heart and blood vessels. It is valuable for assessing valve function, detecting regurgitation or stenosis, and evaluating the presence of abnormal blood flow patterns.
- Color Doppler Imaging:
- This technique uses color to represent the direction and velocity of blood flow. It is particularly useful in identifying turbulent flow, regurgitation, or shunting within the heart.
- 3D Echocardiography:
- Three-dimensional echocardiography provides a more comprehensive view of the heart by creating a three-dimensional image. This can enhance the visualization of complex cardiac structures and improve the understanding of anatomical relationships.
- Strain Imaging:
- Strain imaging assesses the deformation or strain of the heart muscle during contraction. It is useful for detecting subtle changes in myocardial function and can be employed in the evaluation of various cardiac conditions.
- Contrast Echocardiography:
- Contrast agents, typically microbubbles, can be injected to enhance the visibility of certain structures during echocardiography. This technique is particularly helpful in visualizing the endocardium and assessing perfusion.
- Fetal Echocardiography:
- Fetal echocardiography is specifically designed to assess the developing heart of a fetus during pregnancy. It helps detect congenital heart defects and provides crucial information for planning medical interventions after birth.
Once you have found a few good programs, take the time to speak with current or former students to get their opinions on the curriculum, instructors, and overall experience. It is also a good idea to shadow a cardiovascular sonographer in order to see what the day-to-day work entails. This will help you make sure that this is the right career path for you.
The average salary for a cardiovascular sonographer is $63,010 per year, but this can vary depending on experience, location, and other factors. With an aging population and an increase in cardiac related illnesses, there is expected to be a high demand for qualified professionals in this field in the coming years.
How much Cardiovascular Sonography Salary nj
In the field of cardiovascular sonography, New Jersey offers some of the best salaries in the nation. On average, cardiovascular sonographers in New Jersey make $84,520 per year. The top 10% of earners make more than $113,140 per year, and the bottom 10% of earners make less than $55,880 per year.
Cardiovascular sonographers in New Jersey are employed in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, and private practices. Many cardiovascular sonographers choose to specialize in a particular area, such as echocardiography or vascular ultrasound. Sonographers who have completed advanced training and certification may be able to command higher salaries.
What is the Cardiovascular Sonography programs
cardiovascular sonography programs are one of the most popular health care fields.
There are many reasons why people choose to enter this field, but one of the most popular is the potential for a great salary.
cardiovascular sonography programs can lead to careers in hospitals, clinics, or even private practices.
The demand for trained cardiovascular sonographers is expected to grow in the coming years, so now is a great time to enter this field.

How Much Cardiovascular Sonography Operator Salary
Cardiovascular sonography is a non-invasive diagnostic medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the heart and blood vessels. The average salary for a cardiovascular sonographer is $63,630 per year.
Cardiovascular Sonography Programs Near me
If you are interested in a career in cardiovascular sonography, there are several things to consider. One of the most important factors is finding an accredited program that fits your needs and schedule. Here is a list of cardiovascular sonography programs near you:
Cardiovascular Sonography Programs at Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic offers an 11-month accredited cardiovascular sonography program that includes didactic coursework and clinical rotations. The program is designed to prepare students for the ARDMS certification exams.
Cardiovascular Sonography Programs at Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic offers an 18-month accredited cardiovascular sonography program that includes didactic coursework, clinical rotations, and a research project. The program is designed to prepare students for the ARDMS certification exams.
Cardiovascular Sonography Programs at Duke University
Duke University offers a 12-month accredited cardiovascular sonography program that includes didactic coursework and clinical rotations. The program is designed to prepare students for the ARDMS certification exams as well as the Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer (RDMS) credential from the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS).
Easy@Home TENS Unit Muscle Stimulator – Electronic Pulse Massager, 510K Cleared, FSA Eligible OTC Home Use handheld Pain Relief therapy Device-Pain Management Machine Gift for Mom Dad – EHE009

FAQ
What is cardiovascular sonography

Cardiovascular sonography, also known as echocardiography, is a medical imaging technique used to examine the heart’s structures and assess its function. It involves the use of a transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the heart and produce echoes. These echoes are then converted into real-time images of the heart using advanced computer technology.
What is cardiac sonography used for?

An echocardiographer (cardiac sonographer) uses ultrasound equipment to examine a patient’s heart’s chambers, valves, and vessels. When the patient is resting or when they have been physically active, echocardiograms can be performed.
What is the difference between cardiac and cardiovascular sonography?
If you’d prefer to specialize in producing images of just one organ, cardiac sonography is an excellent choice. Medical sonography focuses on other parts of the body.
Which sonographers make the most money?

Sonography of the brain costs $112,000. Pediatric cardiac sonography costs $80,000. Cardiac sonography costs $79,000. Vascular sonography costs $68,000.
What is the difference between ECG and sonography?

ECGs use electrodes to detect abnormalities in the heart’s electrical impulses, while echocardiograms use ultrasound to detect structural anomalies.
Which scan is better for heart?

CT scans of the heart use x-rays to produce detailed pictures of the heart and its blood vessels. They are called coronary calcium scans when they are used to detect calcium buildup in the arteries of the heart.




