Pulmonary Ventilator
Pulmonary Ventilator
Are you familiar with the term pulmonary ventilator? If not, you are about to learn a lot more about this life saving medical device! Pulmonary ventilators have been critical in keeping patients alive during respiratory failure, especially amid the current global health crisis. In this blog post, we will learn about what a pulmonary ventilator is and how it works, as well as its importance in modern medicine. So buckle up your seat belts and get ready for the informative journey ahead.
Types of ventilator
There are many types of ventilators available on the market, and each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of ventilators are:
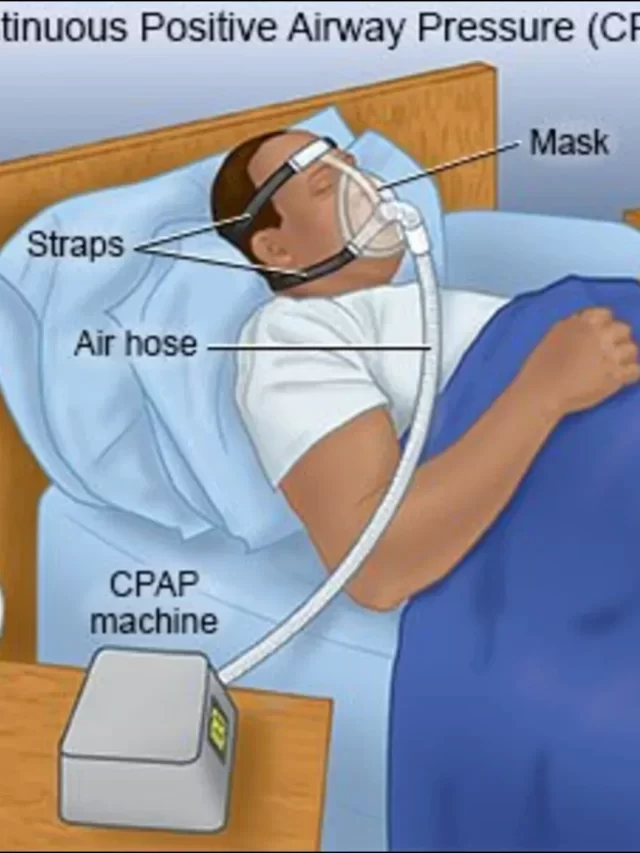
1. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) ventilators: The CPAP ventilator is the most commonly used ventilator in hospitals. They provide a constant stream of air to the lungs, keeping the airways open and preventing collapse. CPAP ventilators are very effective in treating sleep apnea and other breathing disorders.
2. Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) ventilators: BiPAP ventilators are similar to CPAP ventilators, but they provide two levels of air pressure – one for inhalation and one for exhalation. This makes BiPAP ventilators more comfortable to use than CPAP ventilators, and they are often used for patients with COPD or other respiratory disorders that make breathing difficult.
3. Pressure support ventilation (PSV): PSV is a variant of intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV). It delivers small puffs of air into the lungs, giving the patient enough support to breathe on their own. PSV is often used for patients who are unable to tolerate CPAP or BiPAP ventilation.
4. Volume control ventilation (VCV): VCV is another type of IPPV that delivers a set volume of air with each breath . This type of ventilator is often used for patients who require long-term mechanical ventilation.
5. Noninvasive ventilation (NIV): NIV is a type of mechanical ventilation that does not require the patient to have an artificial airway, such as a tracheostomy tube. NIV uses a mask or mouthpiece to deliver air to the patient’s lungs and is most commonly used for patients with COPD or other respiratory disorders.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- IR News
Article About:- Sports

Types of ventilator in ICU
There are many different types of ventilators in the ICU, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. The most common type of ventilator in the ICU is the mechanical ventilator. In this type of ventilator, a machine is used to help the patient breathe. Mechanical ventilators are very effective at helping patients breathe, but they can be uncomfortable and can cause some side effects.
One type of mechanical ventilator is the positive pressure ventilator. This type of ventilator helps the patient by pushing air into the lungs. Positive pressure ventilators are often used for patients who are unable to breathe on their own. They can be uncomfortable for some patients and can cause side effects such as abdominal bloating and nausea.
Another type of mechanical ventilator is the negative pressure ventilator. This type of ventilator helps to draw air out of the patient’s lungs. Negative pressure ventilators are often used for patients who are having trouble breathing. They can be uncomfortable for some patients and can cause side effects such as dizziness and lightheadedness.
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is another type of ventilator commonly used in ICUs. NIV does not require a machine to help the patient breathe. Instead, NIV uses a mask or nasal cannula to deliver oxygen to the patient. NIV is often used for patients who are not able to tolerate a mechanical ventilator or who are not able to get enough oxygen through a mechanical ventilator. NIV can be very effective, but it can also cause side effects such as dry mouth and sore throat.
What is pulmonary ventilation?
Pulmonary ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs. The respiratory system is responsible for pulmonary ventilation. The main organs of the respiratory system are the nose, mouth, trachea, bronchi and lungs. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles also play a role in pulmonary ventilation.
What is a normal pulmonary ventilation rate?
A normal pulmonary ventilation rate is the number of breaths taken per minute by a healthy person. The average adult respiratory rate is 12-20 breaths per minute.
What is pulmonary ventilation more commonly called?
Pulmonary ventilation, commonly referred to as breathing, is the process by which air is drawn into and out of the lungs. The lungs are elastic structures that expand and contract when air comes in and out. This expansion and contraction of the lungs creates negative pressure, which draws air into the lungs.