
What is an autoclave, principle of autoclave, Application of Autoclave
What is an Autoclave ?
Autoclaves, also known colloquially as steam sterilizers, are used in medicine and for industrial applications. An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on objects placed inside a pressurized vessel.
The objects are heated to the appropriate sterilization temperature for a certain amount of time. The moisture in the steam destroys the protein structure of bacteria and spores.
In the healthcare sector, the term autoclave is commonly used to refer to steam sterilizers. ANSI/AAMI4, which provides standards and guidelines for the processing of medical equipment, specifically refers to autoclaves for the medical field as steam sterilizers.
If the history of autoclave is to be done, French-born physicist Denis Papin did it in 1679. After that the autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879.
But, the concept of disinfection and sterilization was introduced by Robert Koch in 1881. Then in 1933 the modern autoclave, the first pressure steam sterilizer with control performance, was developed.
Autoclave items must be adapted to high heat and moisture conditions and processed in accordance with the manufacturer’s written instructions for use. Medical devices that have contact with sterile body tissues or fluids are considered critical items.
These items typically include surgical instruments, implanted medical devices, and surgical drapes and linens. These items must be sterile when using as any microbial contamination can result in infection transmission.
Steam is often the sterilant of choice for the sterilization of heat and moisture stable objects because it is reliable, consistent and non-toxic to microorganisms while being safe for the workers operating the autoclave.
How does an autoclave work?
Autoclaves are commonly used in healthcare settings to sterilize medical equipment. Items to be sterilized are placed inside a pressure vessel called a chamber. Three factors are important to ensure successful steam sterilization in an autoclave, namely time, temperature and steam quality.
The autoclave process has three steps to meet these requirements:
Conditioning Phase (C):- This air prevents sterilization and must be removed from the chamber during the first phase of the sterilization cycle known as conditioning. In Dynamic Air Removal Type Steam Sterilizer air is removed from the chamber using a vacuum system.
It can also be removed without a vacuum system using a series of steam flushes and pressure pulses. Gravity type sterilizers use steam to displace the air in the chamber and push the air down the sterilizer drain.
Exposure phase(s):- The sterilizer drain automatically closes after the air is removed and steam continuously enters the chamber, raising the pressure and temperature rapidly to a predetermined level. The cycle enters the exposure phase and the objects are kept at sterilization temperature for a certain amount of time required to sterilize.
Exhaust stage (E):- During the last stage of the cycle, the exhaust, sterilizer conduit is opened and the steam is removed, depressurizing the vessel and allowing the items in the load to dry in it.
Quality steam is critical to a successful autoclave sterilization process. The steam used for sterilization consists of 97% steam and 3% moisture. This ratio is recommended for the most efficient heat transfer.
When the moisture content of the steam is less than 3%, the steam is described as superheated. Overheated steam is too dry for efficient heat transfer and ineffective for steam sterilization.

What is the principle of autoclave?
Autoclave works on the principle of moist heat sterilization. The high pressure inside the chamber raises the boiling point of water for sterilization of equipment.
Thereby the high pressure also ensures rapid penetration of heat into the deeper parts of the equipment. The moisture present in the steam causes the protein deposition of microbes leading to irreversible loss of their activity and functions.

What should be the autoclave temperature range?
The commonly recommended temperature for steam sterilization is 250 °F (121 °C), 270 °F (132 °C) or 275 °F (135 °C). In order to kill any microorganisms present, the items being sterilized have to be exposed to these temperatures for the minimum amount of time recommended by the manufacturer of the equipment being processed.
What is the autoclave cycle time frame?
Exposure time is the time required to sterilize the equipment and does not include the entire cycle time. Proper steam sterilization has a time/temperature relationship that has been developed by scientific testing and is used in all sterilization methods to create what is known as the total exposure phase.
Exposure periods for steam sterilization vary with the size, shape, weight, density and material composition of the equipment, among other factors.
How big is an autoclave?
The size of the sterilizer varies depending on the requirement where autoclaves are used. For example, a small autoclave in a dental clinic may simply sit on the countertop where equipment is only needed to sterilize small packs of equipment.
An immediate-use small sterilizer is needed near an operating room, and may only need to process 1-3 trays of equipment at a time. Most healthcare facilities have medium or large autoclave machines in their sterile processing department that can process 15-20 trays of equipment per cycle or up to 625 lbs of equipment per cycle, depending on size.
Industrial-sized autoclaves can be too large for manufacturing processes, some even being the size of a semi-truck or airplane.
How much does an autoclave cost?
The cost of an autoclave can vary greatly due to the different uses and applications of this technology. Industrial and pharmaceutical autoclaves are customized and manufactured for a specific use and therefore cost different than autoclaves found in a hospital or dental clinic.
The cost of an autoclave in healthcare applications varies according to capacity and installation method. Beyond the initial cost of the autoclave, the maintenance and cost of sterility assurance and monitoring products must be considered.
Depending on the autoclave manufacturer, cost per cycle, utility consumption and maintenance cost can vary over time and should be evaluated to compare your total cost of ownership over time.
Industrial Autoclave Vs. medical autoclave
Autoclaves are used in a variety of industrial and medical applications. Industrial autoclaves are used in manufacturing environments to process parts and materials using hot steam and pressure.
For example, in the manufacture of pressure treated wood and the special rubber used in your car tires. Autoclaves are also used in the scientific research and pharmaceutical industries.
Beyond sterilizing equipment used in laboratory research, most autoclaves are equipped with a liquid cycle to sterilize liquids used in laboratory environments.
Medical Steam Sterilizer can be used for the sterilization of heat and moisture stable objects such as surgical instruments, implanted medical instruments and surgical drapes and linens in healthcare environments.
The cycles used in Medical Steam Sterilizers are developed and validated in accordance with recognized industry standards.
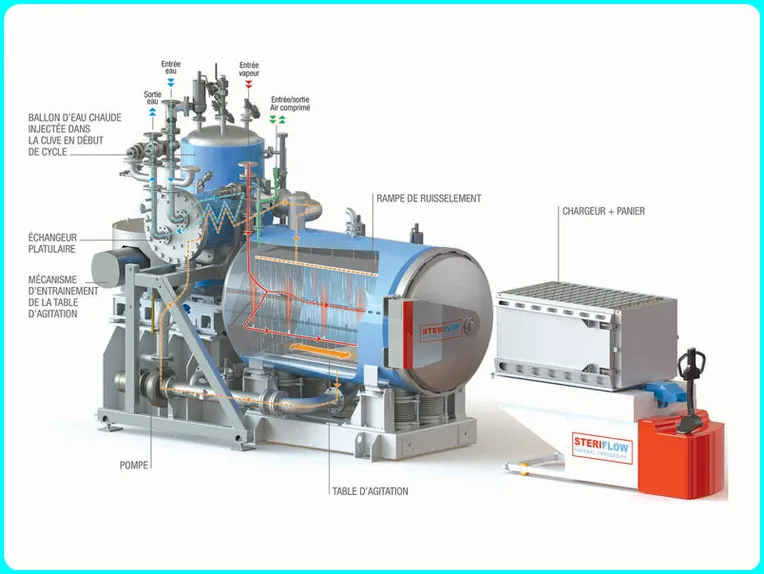
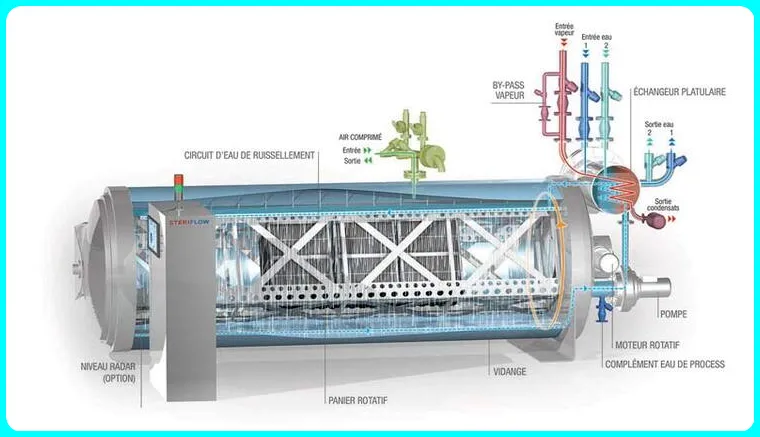
Horizontal Autoclave Control Equipment:
Temperature Controller :- It consists of a microprocessor based PID controller which includes temperature, timer with buzzer alarm. The controller has a double LED display for set and process values with a time of 9999 minutes.
21 CFR controllers display the F0 value without any manipulation with the online data recording feature. 15 minutes at 121.1 degrees gives an F0 value of 15 points.
It is an important factor in the sterilization of surgical instruments in the medical field these days.

Pressure regulator
Scientific provides a built-in pressure controller to protect the user and the autoclave. It is used that the pressure controller cuts off the heater’s power supply when it reaches the set value.
Doors
In this, the sterilizer can be designed as single door or double door with radial locking provision. Negative or positive pressure does not allow the door to open until atmospheric pressure arrives.
Trolley
The trolley should be designed in stainless steel or mild steel with SS wheels for easy maneuverability. Trolley is a very essential part of horizontal sterilizer which prevents material from getting contaminated.
Multi-port valve
Multi-port valve controls steam purging speed, steam transfer from jacket to chamber, vacuum exhaust, slow exhaust.
Moisture trap
When the multi-port valve transfers steam from the jacket to the sterilization chamber during the sterilization cycle, there is a moisture trap designed to remove cold moisture from the chamber.
Vacuum breaker
In this the condensed steam creates a vacuum inside the chamber and the jacket and vacuum breaker protect the user and the machine from shrinkage. Vacuum breakers are installed at the top for the sterilization chamber and at the other for the jacket. All pipe connections are made of SS304/SS316 of BSP standard.
Emergency on/off
This releases all the steam pressure from the chamber by opening all the solenoid valves in an emergency. This happens to be one of the safety features of a horizontal sterilizer.
Steam Generator / Boiler
The steam generator sterilization chamber is designed according to the size capacity.
The boilers are manufactured with ISI mark U shape water heater with low water cut off system and glass window for water level indicator.
High speed type
A high speed term is used for a faster sterilization cycle by increasing the load of the horizontal autoclave. Hospital operation theaters require high-speed autoclaves for the sterilization of surgical instruments.
Type of autoclave
1.) Pressure Cooker Type or Laboratory Bench Autoclave (N-Type):- This is a home pressure cooker that is perfect for tissue culture enthusiasts or hobbyists.
2.) Gravitational Displacement Type Autoclave:- This is the most common type of autoclave used in research laboratories. In this autoclave, steam continues to displace the air in the chamber by gravity through a drain port.
3.) Positive Pressure Displacement Type (B-Type):- It is an advanced type of autoclave, in which steam is generated in a separate steam generator, which is then passed into the autoclave for sterilization of equipment.
4.) Negative Pressure Displacement Type (S-Type):- This is the most expensive type of autoclave. It comes with a vacuum generator and steam generator which works efficiently to achieve complete sterilization of the equipment.
Horizontal autoclave
Typically processing light loads often in the laboratory, the front-loading horizontal autoclave is perfect for reducing stress and repetitive injury to technicians who handle multiple loads in a day.
Media preparation
This autoclave enables the preparation and sterilization of microbiological media. Media precipitators are available in a range of sizes from 10L to 120L and process cycles quickly and accurately combined with accelerated cooling options.
Pass-through autoclave
Having a pass-through autoclave is a must when safety and contamination are a concern. This autoclave is mostly found in biological laboratories and production facilities.
The pass-through autoclave serves as a sterilization chamber that enables the transfer of materials and products from the laboratory to the outdoor environment safely.
The machine is located on the laboratory side of the side wall. Where various items are loaded for the sterilization process and can be obtained on the other side, as clean and free of contaminants.
Vertical autoclave
Specially developed for laboratory sterilization applications, vertical autoclaves make the process easier, safer, more accurate, reproducible and easier to validate.
The compact and space-saving design of vertical autoclaves makes them great for cramped laboratories, where space is at a premium, and the increased chamber height means they can handle most standard media bottles.
What are the precautions to be taken while using autoclave?
- Waterproof or water-resistant materials such as oils or powders must not be sterilized.
- Overload the autoclave with the vessel and equipment. Sterilize your equipment as low as possible, if possible.
- Only autoclavable bags should be used for autoclave package waste.
- Use autoclavable bags to sterilize your equipment. Never use aluminum foil in this.
- Do not fill the autoclave chamber to the lid.
- Never attempt to open the autoclave while it is operating.
- Close the lid tightly to ensure the fully closed position of the autoclave for proper sterilization.
- Do not use regular plastic or trays in autoclaves.
- Never autoclave flammable, reactive, corrosive, toxic, or radioactive material, household bleach, or paraffin-embedded tissue.
- Fill the steam generator with water to the point where it touches the end of the pot or the chamber of the autoclave.
Application of Autoclave
1.) hospital
2.) mushroom spawn production
3.) pharmaceutical factory
4.) food industry
5.) chemical industry
6.) Universities
7.) Medical Center
8.) research institutes
9.) Animal Testing Labs
10.) Primary Health Centre
11.) test facility

FAQ
What is a autoclave used for?

Autoclaves use high pressure and warmth to kill spores and germs. They are used to sterilise lab equipment, sterilise media, and decontaminate specific biological waste.
What is called autoclave? and What is an autoclave

Steam sterilisers, or autoclaves, are frequently employed in the healthcare or industrial sectors. A device known as an autoclave employs steam under pressure to destroy dangerous bacteria, viruses, fungus, and spores on objects that are placed inside a pressure vessel.
What is autoclave definition and principle?

A device known as an autoclave uses the moist heat sterilisation (MHS) method to kill bacteria, viruses, and even heat-resistant endospores on a variety of instruments by creating saturated steam under pressure.
What is autoclave temperature?

In order to reach a chamber temperature of at least 250°F (121°C) for a set amount of time—typically 30–60 minutes—autoclaves employ saturated steam under pressure of around 15 pounds per square inch. In addition to the right temperature and amount of time, avoiding air entrapment is essential for establishing sterility.
What are the 4 types of sterilization?

High-pressure steam (autoclave), dry heat (oven), chemical sterilants (glutaraldehyde or formaldehyde solutions), or physical agents (radiation) can all be used to achieve this. Sterilisation is a process, not an event, hence all steps must be followed precisely for sterilisation to take place.
What are the parts of autoclave?

Important Elements of an Autoclave Vessel. The autoclave’s basic structure, the vessel, is made up of an inner chamber and an outside jacket. … Vacuum System (if applicable);… Thermostatic Trap;… Safety Valve;… Waste-Water Cooling Mechanism;… Steam Generator (if applicable)
Why is 121 degrees used in autoclave?

Because endospores are not killed at 100oC (the temperature at which water will boil under ideal atmospheric circumstances), sterilisation cannot be entirely accomplished. Geobacillus stearothermophilus is really employed as an indicator to show when a sterilisation cycle has been successful.
Which law is used in autoclave?

Boyle’s law is the foundation of how an autoclave operates.
It should be possible to replace all of the chamber’s air with steam. The environment must be 121 °C.
What are the 3 types of sterilization?

There are only a few key physical and chemical processes that are used to properly sterilise equipment, despite the fact that there are many of both. Having stated that, the scientific community uses three primary categories of sterilisation techniques nowadays. They are sterilisation with steam, dry heat, and ethylene oxide (EtO).
What are the 3 stages of autoclave sterilization?

The Cycle of Steam Sterilisation in Detail
Conditioning, exposure, and drying are the three separate processes that make up steam sterilisation cycles. Air is taken out of the load during conditioning, and the load’s contents are heated to the necessary sterilisation temperature.









