
What is Capnography?
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the respiratory gases. It provides physiological information on ventilation and metabolism, which is important for airway management. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care.
Capnography is part of a paramedic’s toolkit. Recent surveys indicate that upwards of 90–95 percent agree that capnography is easy to understand and an important monitoring tool for patients with cardiac arrest who are experiencing respiratory distress, or sick with sepsis.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
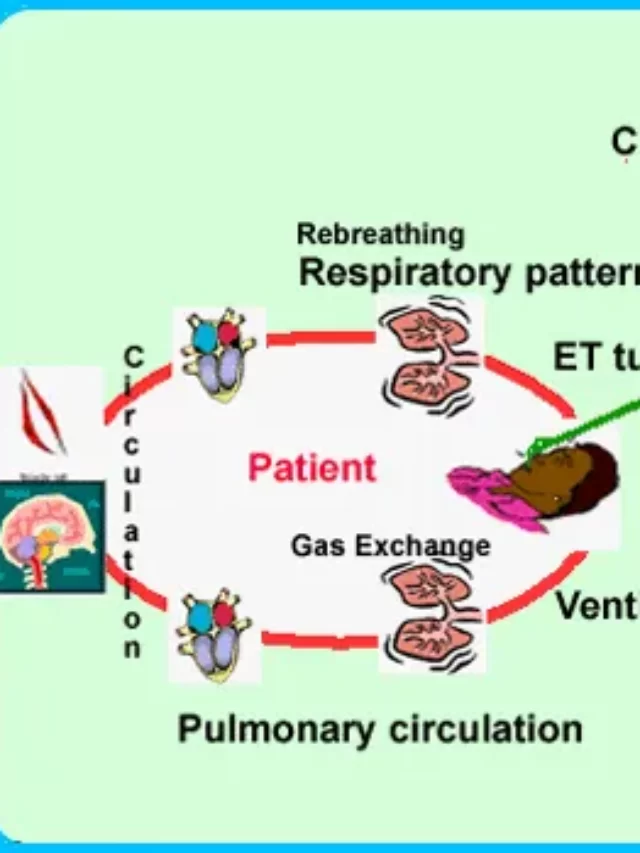
The Capnogram is a direct monitor of the inhalation and exhalation concentration or partial pressure of CO, and an indirect monitor of the CO2 partial pressure in arterial blood. In healthy individuals, the difference between the partial pressure of arterial blood and the exhaust gas CO2 is very small.
Capnography is the measurement of carbon dioxide in a patient’s exhalation over time. Commonly used during anesthesia procedures, capnography is increasingly being used by paramedics in the field for a variety of purposes, including evaluating the success of resuscitation efforts, confirming clinical death, and causing respiratory distress.
Waveform Capnography/ Capnography Waveforms
Waveform capnography is a fine monitoring technique used to measure and analyze the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) when a patient exhales. It provides valuable information about the patient’s respiratory status and can help assess ventilation and perfusion.
During waveform capnography, a small sample of exhaled breath is captured and analyzed for its CO2 content. The resulting data is represented as a graphical waveform called a capnogram. The capnogram shows the change in CO2 concentration over time during the respiratory cycle.
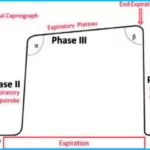
The capnogram waveform typically consists of several phases, including the following:
Baseline: Baseline represents the early phase of the wave, where CO2 concentrations are low and stable. This corresponds to the end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2) level during the termination break.
Phase I: Also known as the “physiological dead space” phase, Phase I represents the initial part of exhalation. It shows a rapid rise in CO2 concentration as dead space gases, which have lower CO2 concentrations, are ejected.
Phase II: Phase II is a transitional phase that occurs after Phase I. It refers to a mixture of dead space gases and alveolar gases with intermediate CO2 concentrations. The slope of phase II is steeper than that of phase I.
Phase III: Phase III corresponds to the alveolar plateau, where CO2 concentration reaches its peak. This represents the end-tidal CO2 level and reflects the CO2 concentration in the alveoli at the end of exhalation.
Phase 0: After Phase III, there is a rapid decline in CO2 concentration during the respiratory phase. This phase is sometimes called phase 0, and it represents inspiration.
Analysis of the capnogram waveform can provide important information about the patient’s respiratory status. Key parameters obtained from waveform capnography include:
End-tidal CO2 (EtCO2): The highest value of CO2 concentration during expiration is measured at the end of stage III. EtCO2 is used as an estimate of the arterial CO2 (PaCO2) level.
Respiratory rate: The number of complete respiratory cycles per minute, which can be determined by analyzing the capnogram waveform.
Waveform shape: Irregularities or abnormalities in the waveform shape may indicate various respiratory conditions or mechanical issues such as airway obstruction, bronchospasm, or faulty equipment.
Waveform capnography is widely used in a variety of clinical settings, including operating rooms, intensive care units (ICUs), emergency departments, and pre-hospital settings. It helps in the early detection of respiratory complications, monitoring the effectiveness of ventilation, assessing the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), and guiding the titration of mechanical ventilation.
Capnography Monitor
A capnography monitor is a medical device used to measure and display the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in a patient’s breath in real time. It provides continuous monitoring of a patient’s respiratory status and is commonly used in various health care settings including hospitals, clinics, and ambulances.
Capnography monitors have a display screen that shows the capnogram waveform, which represents the change in CO2 concentration over time during the respiratory cycle. Additionally, the monitor can display numerical values for parameters such as end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2), respiratory rate, and other relevant measurements.
Capnography monitors typically use one of two main types of sensors to measure CO2:
- Mainstream capnography: In mainstream capnography, a CO2 sensor is placed directly into the patient’s breathing circuit. This type of sensor is located close to the patient’s airway, usually between an endotracheal tube or mask and a mechanical ventilation device. Mainstream capnography provides real-time measurements and is commonly used during surgery and in critical care settings.
2. Sidestream capnography: In sidestream capnography, the CO2 sensor is positioned away from the patient’s airway, and a small sample of the patient’s breath is drawn through a tube to the sensor for analysis. The sample is taken through a sampling line, which can be connected to various airway interfaces, such as a nasal cannula or a mask. Sidestream capnography is more portable and versatile, allowing monitoring in different patient care areas and during transport.
Capnography monitors offer several advantages in patient care, including:
- Assessment of ventilation: Capnography provides information about the patient’s exhaled CO2 levels, which can help evaluate the adequacy of ventilation and detect conditions such as hypoventilation or hyperventilation.
2. Confirmation of Endotracheal Tube Placement: Captography is commonly used to verify correct placement of an endotracheal tube during intubation. This helps to differentiate between proper placement in the trachea versus accidental insertion into the esophagus or bronchus.
3. Monitoring during procedural sedation: Capnographi is especially useful during procedures involving conscious sedation or anesthesia, as it can quickly detect respiratory depression and airway obstruction.
4. Detection of respiratory distress: Capnographi can help identify conditions such as airway obstruction, bronchospasm, or respiratory compromise, allowing for early intervention.
Overall, capnogrephi monitors play an important role in assessing and managing a patient’s respiratory status, aiding in the timely detection of respiratory complications and optimizing patient care.
How to Capnography work?
One utility of carbon dioxide (CO2) is that it absorbs infrared radiation. When the patient exhales, a beam of infrared light is passed over the gas sample on the sensor.
In this, low CO2 levels result in high amounts of light, while high CO2 levels are indicated by low infrared. The presence or lack of CO2 is indicated inversely by the amount of light passing through the sensor.
In the presence of most forms of lung disease and some forms of congenital heart disease, the difference between arterial blood and expired gas increases and may exceed 1 kPa.

CO2 levels are then displayed on the detector and adjusted for the presence of nitrous oxide, which can also absorb infrared rays and thus cause some confusion if not accounted for.
What is measured by the capnograph is known as end tidal CO2, or the amount (or partial pressure) of carbon dioxide released at the end of expiration, which is needed to assess cardiac output.
Why is capnography so important?
CO2 levels in the blood are incredibly important for proper oxygenation and metabolism, which is why capogrephy is so useful. The irregular amount of CO2 in a patient’s breath and the amount of that irregularity can tell health care providers a lot about the condition and treatment needed.
In hospitals, capnogrephy has traditionally been used during anesthesia, where it monitors metabolic processes through CO levels, both depleted and arterial.

Capnography helps to identify conditions that can lead to hypoxia. Furthermore, it helps in the rapid differential diagnosis of hypoxia before hypoxia leads to irreversible brain damage.
Because of these benefits, the usefulness of capnography has recently been extended to on-site emergency and trauma areas outside the area of emergency rooms, endoscopic suites, X-ray rooms, and even operating rooms.
ETCO2 levels are highly indicative of the effectiveness of chest compressions during CPR, and may be the first indicator of the return of spontaneous circulation.
In addition, capnogrephy is used to analyze the causes of respiratory distress in patients, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or bronchitis. It can also provide early warning signs of hypoventilation or airway obstruction before any changes are seen in the heart rate or blood pressure monitor.
Capnogrephy is an incredibly effective way to identify low perfusion, as ETCO2 levels can also provide early warning signs of shock. And finally, capnography may also provide a way to determine when resuscitation efforts can reasonably stop in other words, certain ETCO2 activity levels may serve as confirmation of clinical death.
Advantage of Capnography
The transmission of airflow is a surrogate measure, such as impedance basing, that the aircraft can apply as a ‘correction’ to climate change. Due to the favorable weather conditions it is in, it will be better suited to the better weather as well.
Disadvantage of Capnography
Compliance and especially of ‘scoop’ cannula, which are essential when needed such as S sensitive, apnea, and are less sensitive when disease requires it to be included.

FAQ
what does capnography measure
Capnographi is part of a paramedic’s toolkit. Recent surveys indicate that upwards of 90–95 percent agree that capnography is easy to understand and an important monitoring tool for patients with cardiac arrest who are experiencing respiratory distress, or sick with sepsis.
what is the capnography waveform a graphical representation of
One utility of carbon dioxide (CO2) is that it absorbs infrared radiation. When the patient exhales, a beam of infrared light is passed over the gas sample on the sensor.
What is the purpose of a capnography?

Capnogrephy is an effective method to diagnose early respiratory depression and airway disorders, especially during sedation, leading to a reduction in serious complications (23, 24). Capnogrephy provided more safety in monitoring patients during sedation.
What are the 2 types of capnography?

Inspiration, therefore, is shown on the waveform by a drop of the CO2 levels to zero. The process is relatively simple, as is the equipment. There are two types of capnogrephy, mainstream and sidestream.
What are 3 uses of capnography?

Capnography has several roles at cardiac arrest:
Confirmation that the airway is patent and present within the trachea.
Monitoring ventilation rate during CPR and avoiding hyperventilation.
Assessing adequacy of chest compressions during CPR.
Identifying return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) during CPR.
How is capnography measured?
Capnogrephy measures ventilation through a metric known as end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2). EtCO2 values are recorded in mm Hg (millimeters of mercury), a unit of pressure. The normal values for patients regardless of age, sex, race, or size range between 35-45 mm Hg, or about 5% CO2.
What instrument is used for capnography?
A capnograph is an instrument that measures the carbon dioxide concentration in an air sample. It is most commonly used to monitor the carbon dioxide content of air being delivered to intensive care patients or those under anesthesia.
What are the CO2 levels in capnography?

35-45 mm Hg
Capnogrephy provides breath-to-breath ventilation data
This is end-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) which is normally 35-45 mm Hg. The capnograph is the waveform that shows how much CO2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle, and it normally has a rectangular shape.
Why is capnography used in CPR?

Measurement of end-tidal expiratory pressure of carbon dioxide (ETCO2) using capnography provides a noninvasive estimate of cardiac output and organ perfusion during cardiac arrest and can therefore be used to monitor the quality of CPR and predict return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
what is waveform capnography

Waveform capnography is a fine monitoring technique used to measure and analyze the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) when a patient exhales. It provides valuable information about the patient’s respiratory status and can help assess ventilation and perfusion.
what is true of quantitative waveform capnography

Quantitative waveform capnography refers to the measurement and analysis of carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in exhaled breath using a capnography monitor that provides a numerical value for end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2).
1. Numerical Measurement.
2. Waveform Analysis.
3. Accurate Monitoring.
4. Ventilation Assessment.
5. Patient Safety.












