
How to Work Ophthalmoscope
Ophthalmoscopy is used to understand the structure of the eye and to look inside the fundus of one eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope. Commonly used to examine retinal and vitreous humor.
With the help of ophthalmoscope, doctors can diagnose the disease properly as well as treat it.
Basic components of Ophthalmoscop
| Patient side | User side |
| 1. Lens | 1. Light |
| 2. Eye rest | 2. Vertical dial |
| 3. Vertical dial | 3. Horizontal dial |
| 4. Red button | |
| 5. Power base | |
| 6. Number settings | |
| 7. Lens | |
| 8. Eye rest | |
| 9. Vertical dial | |
| 10. Red button | |
| 11. Power base | |
| 12. Number settings |
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:-Sports
Types
1. Direct ophthalmoscope
2. Indirect ophthalmoscope

Direct ophthalmoscope
a. Image produced will be upright, or unreversed
b. Approximately 15 times magnification
Direct ophthalmoscope is the easiest instrument of choice by physicians for fundus examination. This allows a magnified, monocular image of the retina and optic disc.
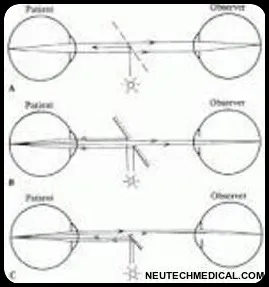
Direct ophthalmoscope working principle

In direct ophthalmoscopy if the eye is emmetropic, light rays emanating from a point in the fundus emerge as parallel beams. If this beam enters the pupil of an emmetropic observer, the rays are focused on the retina of the observer and form an image of the patient’s retina on the retina of the observer. This is called direct ophthalmoscopy.
a. Image produced will be inversed, or reversed
b. Approximately 2 to 5 times magnification
It is called indirect ophthalmoscopy because, BIO is one of the methods used to view the retina, which has a wide field of view and stereoscopic view of the retina. The BIO device also allows dynamic observation of the retina by moving the lens and applying scleral depression.
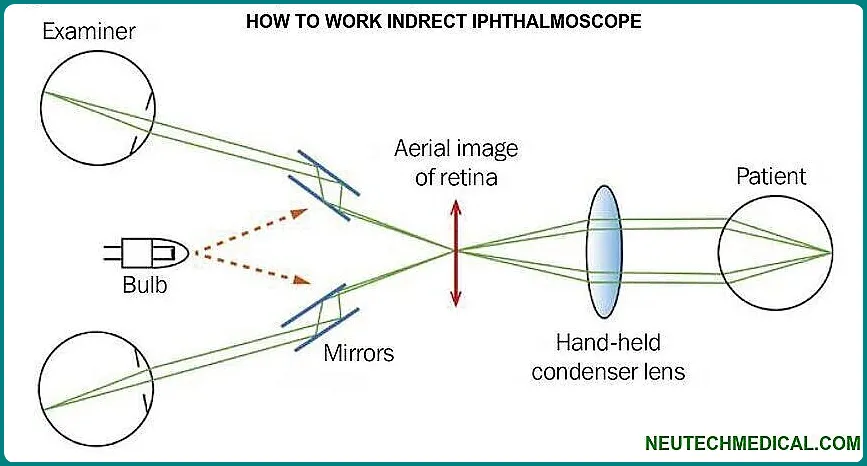
The procedure is “indirect” because the fundus is viewed through a hand-held condensing lens. Its main use is the binocular indirect ophthalmoscope, an optical instrument worn on the examiner’s head, and sometimes attached to glasses, which are used to observe the fundus or the back of the eye. This produces a stereoscopic image with 2x and 5x magnification.
Indirect Ophthalmoscop Principle
The main principal of indirect ophthalmoscopy is, in short, the purpose of the ophthalmoscopy lens in indirect ophthalmoscopy is to redirect the diverging pencil of light from the patient’s pupil towards the observer’s eye. In doing so, the lens focuses parallel rays within each pencil into an inverted aerial image of the patient’s fundus.
What are the Ophthalmoscope Vs Otoscope
An ophthalmoscopy and an otoscope are both medical instruments used to examine your eyes. Here is a comparison between the two:
Ophthalmoscope:
- Purpose: The ophthalmoscope is used to examine the internal structures of the eye, such as the retina, optic nerve, blood vessels, and macula.
- Components: This usually consists of a light source, a power control dial, a lens wheel, and a viewing hole.
- Examination techniques: Ophthalmoscopy involves illuminating the eye and observing the fundus (the back of the eye) through an ophthalmoscope using various lenses and focusing techniques.
- Common Users: Ophthalmologists, optometrists, and some specialty nurses are the primary users of ophthalmoscopes.
Otoscope:
- Purpose: An otoscope is used to examine the ear, specifically the outer ear canal and tympanic membrane (eardrum).
- Components: It consists of a light source, a magnifying lens, and a speculum (a cone-shaped attachment for entering the ear canal).
- Examination Technique: Otoscopy involves gently inserting the speculum of the otoscope into the ear canal and examining the structures of the ear, including the ear canal, eardrum, and possibly the middle ear.
- Common Users: Physicians, otolaryngologists (ear, nose, and throat specialists), and other health care professionals use otoscopes to assess ear health and diagnose conditions such as ear infections, earwax buildup, or eardrum abnormalities.
In brief, ophthalmoscopy is used to examine the eyes, while otoscope is used to examine the ears. Each instrument is specifically designed to provide optimal visualization and evaluation of the relevant anatomical structures.
Difference between Direct Ophthalmoscope and Indirect Ophthalmoscope

The main difference between the two is as follows, direct ophthalmoscopy is one that produces a straight, or inverted image of about 15 times magnification. Indirect ophthalmoscopy is one that produces an reserved or inverted image at 2 to 5 times magnification.
Features
| Direct ophthalmoscop | Indirect ophthalmoscop |
| a. Good magnification | a. Good for peripheral retina assessment |
| b. Good macular assessment | b. Good for various retinal procedures |
| c. Light and portable | |
| d. Easy to use | |
| e. Size compactable |
Opthalmoscope Use and Importance
Ophthalmoscopy is a test that allows your ophthalmologist, or eye doctor, to see the back of your eye. This part of your eye is called the fundus, and includes the retinal optic disc.
Ophthalmoscopes are used to detect and evaluate symptoms of retinal detachment or eye diseases such as glaucoma. Ophthalmoscopy may also be done if the patient has signs or symptoms of high blood pressure, diabetes, or other diseases that affect the blood vessels.
Mostly concave mirrors are used in optical instruments such as ophthelmoscopes. Ophthalmoscopy consists of a concave mirror with a hole in the middle. The user focuses through a small hole in the back of the concave mirror while a light beam is directed into the patient’s eyeball.
FAQ
How to use ophthalmoscope
Using an ophthalmoscopy requires practice and familiarity with the instrument.
Familiarize yourself with the parts.
Prepare the patient.
Adjust the ophthalmoscope settings.
Position yourself and the patient.
Illuminate the eye.
Approach the eye.
Use the red reflex.
How to use an ophthalmoscope
Using an ophthalmoscopy requires practice and familiarity with the instrument.
Familiarize Yourself with the Ophthalmoscope.
Prepare the Patient and the Environment.
Adjust the Ophthalmoscope.
Approach the Patient.
Illuminate the Eye.
Positioning the Ophthalmoscope.
Start Examination..
Observe the Fundus.
Switch Eyes.
Documentation.
Which technique by the nurse demonstrates proper use of the ophthalmoscope?
A nurse demonstrating proper use of the ophthalmoscopy should follow these techniques:
Proper Hand Positioning.
Correct Patient Positioning.
Appropriate Lighting.
Communication and Patient Comfort.
Eye Illumination.
Lens Selection.
How much does a ophthalmoscope cost
Basic ophthelmoscopes, without additional features or advanced functionalities, are typically more affordable and may cost between $100 and $200. These models are suitable for basic examinations and may be suitable for students or healthcare professionals who are just starting their practice.
Which type of examination requires an ophthalmoscope?
An ophthalmoscopy is primarily used for conducting an examination of the eye’s interior, specifically the structures at the back of the eye, including the retina, optic disc, blood vessels, and macula. This examination is called ophthalmoscopy or fundoscopy.









