
Stents and Angioplasty
Stents and angioplasty are both medical procedures used to treat blockages in blood vessels, typically in the coronary arteries of the heart. Let take a closer look at each of them:
Angioplasty: Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure performed to widen narrowed or blocked arteries. It is most commonly used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. During the procedure, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery, usually in the groin or wrist, and threaded to the site of the blockage. The catheter has a small balloon at its tip, which is inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, thereby opening up the artery and restoring blood flow. This process is called balloon angioplasty.
Stents: A stent is a small, mesh-like tube that is often used in conjunction with angioplasty. It is placed inside the artery at the site of the blockage to help keep the artery open and maintain adequate blood flow. Stents can be made of metal or a combination of metal and fabric. When a stent is used, it is typically inserted into the artery after the balloon angioplasty has been performed. The stent is expanded by inflating the balloon, and then the balloon is deflated and removed, leaving the stent in place. Over time, the body’s natural healing processes cause the stent to become embedded in the artery wall.
Stents are beneficial because they help prevent the artery from re-narrowing, a condition known as restenosis. Some stents are also coated with medication (drug-eluting stents) that is slowly released over time to further reduce the risk of restenosis.
Both Stents and Angioplasty placement are usually performed under local anesthesia, meaning the patient is awake but numbed in the area where the catheter is inserted. These procedures are less invasive compared to traditional open-heart surgery and typically have a shorter recovery time.
It’s important to note that while Stents and Angioplasty can effectively treat blockages and improve blood flow, they are not a cure for underlying conditions like atherosclerosis (plaque buildup). Lifestyle modifications and medication may still be necessary to manage the underlying causes and reduce the risk of future blockages. If you have specific concerns or questions about these procedures, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized information and guidance.
What is Stents and Angioplasty
Angioplasti is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called coronary arteries. In this, a coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that is placed inside a coronary artery. Most often a stent is placed during or shortly after angioplasty.
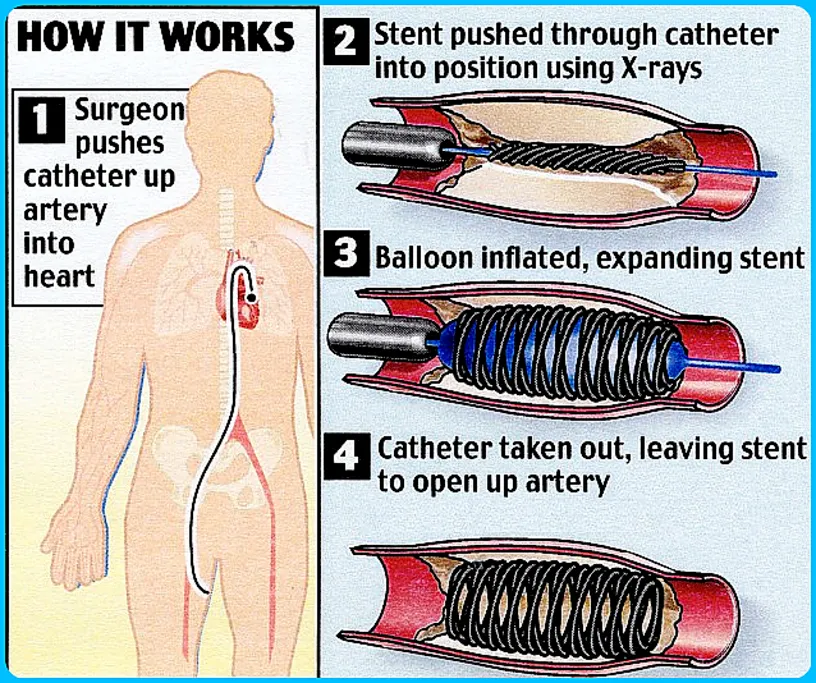
Angioplasti, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins and restore blood flow.
A thin tube is threaded through a blood vessel in the arm or groin up to the involved site in the artery. The tube has a tiny balloon on the end.
When the tube is in place, the balloon is inflated to push the plaque outward against the wall of the artery. This widens the artery and restores blood flow. Sometimes you may need one or more stents to keep the artery from re-narrowing.
A stent is a tiny coil of wire mesh, which is collapsed around a balloon at the tip of the catheter. It is guided through the artery to the blockage.
There, the balloon is inflated, and the spring-like stent expands and locks into place inside the artery. The stent stays in the artery permanently to hold it open and improve blood flow to your heart. Once the stent is in place, the balloon catheter is deflated and removed. ptca, angioplasty procedure, balloon angioplasty
Risk
- Blood clots and bleeding
- Heart attack or stroke
- Coronary artery damage
- Kidney problems
- Abnormal heart rhythms
The primary success rate was 96–98% (100% for stenosis and 92% for total blockages). Treatment modalities included balloon angioplasti (PTA) alone (18%), stent implantation (80%), rotational thrombectomy (2%) and atherectomy (1%).
Stenting is a minimally invasive procedure. Some people are able to leave the hospital after the procedure for stenting. Most people are able to return to work and their normal routines after about a week. Those who do a lot of physical labor have to wait longer.
Is a Stent a Serious Procedure?
Other arteries may also become weak or narrow in the future, which is treated with further stents. Carotid stenting is a serious procedure that requires hospitalization. Although it is a procedure performed by a qualified and experienced physician, it is a commonly performed and relatively safe procedure.
How long does Stents and Angioplasty take?
If a stent is being used, it is placed around the balloon before it is inserted. When the balloon is inflated, the stent expands and when the balloon is inflated and removed, the stent remains in place. A coronary angioplasty usually takes 30 minutes to 2 hours.

What does angioplasty cost
The average cost of an angioplasti procedure is around $1500 to $2000. However, the cost may vary with hospitals and cities. If someone is seeing symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath, then see a doctor immediately.
Advantages of Angioplasty
1.) It can save your life during a heart attack by restoring blood flow to the heart and reducing damage to the heart muscle.
2.) It can quickly reduce symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, making you feel better.
Disadvantages of Angioplasty
1.) Re-narrowing of your artery. When angioplasty is combined with drug-eluting stent placement, there is a small risk that the treated artery may become clogged again.
2.) Blood clots can form within the stent even after the procedure.
3.) Bleeding may occur.
What is the difference between angioplasty and stents?
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called coronary arteries. A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that extends inside a coronary artery. Stents are often placed during or immediately after angioplasty.
How long does angioplasty with stent last?

How long will a stent last? It is permanent. There is only a 2-3 percent risk of the contracture coming back, and if it does it is usually within 6-9 months. If this occurs, it can potentially be treated with another stent.
Is angioplasty a major surgery?

Angioplasty is not considered a major surgery. These procedures are often performed under conscious or moderate sedation in a cardiovascular catheterization laboratory, also known as a ‘cath lab’.
How many stents can be placed in angioplasty?

In answer to your first question, in some cases doctors can place two or even three stents during one procedure. There are, however, cases in which the cardiologist will want to place one and then place a second or even a third stent in a later procedure.
Is angioplasty done without stent?

The word “angioplasty” means using a balloon to open a compressed or blocked artery. However, most modern angioplasty processes also include inserting a small wire mesh tube called a stent in the artery during the process.
What happens to stents after 10 years?

The stent is made to be permanent and will continue to keep your artery open after being placed once. However, stents do not fix the underlying condition that causes buildup in your artery (atherosclerosis). You will still need treatment to prevent future arterial narrowness.
Can you live a normal life after having a stent?

One can go back to their normal routine within 2 to 3 days after undergoing the procedure, depending on the doctors’ recommendations. However, patients who undergo this procedure must ensure they follow the above-mentioned lifestyle changes to lead a long and healthy life after stent placement.
Which is better bypass or stent?

A narrowing or blockage in the LAD is more serious than narrowing or blockage in the other arteries. Bypass surgery usually is the best choice for a blocked LAD. If the LAD is not blocked, and there are no other complicating factors, stents are more likely to be used, even if both of the other arteries are blocked.







